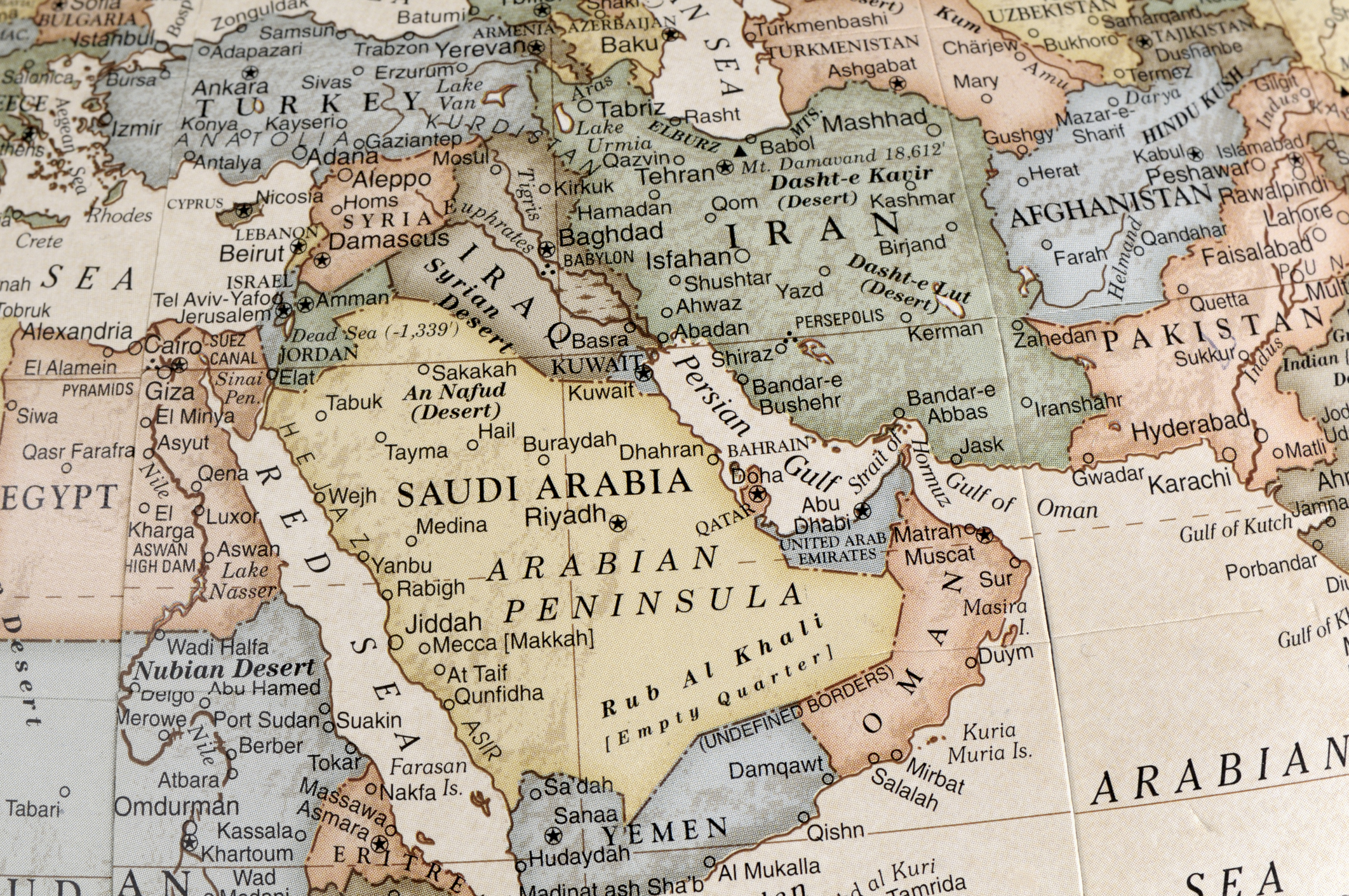
India’s role in shaping the Middle East is rooted in a historical context that dates back to ancient times. Throughout the centuries, India has had significant relations with the Middle East, characterized by trade routes, cultural exchanges, and interactions with various Islamic empires. These historical ties have laid the foundation for India’s past and present involvement in the region.
In the past, India played a crucial role in shaping the Middle East through its non-alignment policy, support for the Palestinian cause, and defense and security cooperation with Middle Eastern nations. India’s commitment to non-alignment, particularly during the Cold War era, positioned it as a key player in the Non-Aligned Movement and allowed it to maintain strong relations with countries like Egypt under Nasserism.
India’s support for the Palestinian cause has been a consistent pillar of its foreign policy, advocating for the rights of the Palestinian people and advocating for a two-state solution. Defense and security cooperation with Middle Eastern countries, such as in the case of India’s relationship with Israel, have further strengthened India’s presence in the region.
In the present day, India continues its engagement in the Middle East through various dimensions. This includes economic and energy partnerships, as India is one of the largest importers of oil from the Middle East. Political and diplomatic relations are also a significant aspect of India’s engagement, with India fostering ties with countries in the region through high-level visits, strategic dialogues, and mutual cooperation on regional and global issues.
India is expanding cultural ties with the Middle East, promoting people-to-people exchanges, cultural programs, and educational collaborations. This has served as a bridge to enhance understanding and strengthen bilateral relations.
Several geopolitical factors shape India’s role in the Middle East, including energy security concerns, counter-terrorism cooperation, and the need to navigate regional conflicts. India’s growing energy demands make securing energy resources from the Middle East crucial. Cooperation on counter-terrorism initiatives is essential to address mutual security challenges. India also navigates regional conflicts in the Middle East with careful diplomacy to maintain its relations with all parties involved.
While India’s engagement in the Middle East presents opportunities, it also faces challenges. Competition from other global players seeking influence in the region, the need to balance ties with different Middle Eastern states, and leveraging soft power and cultural diplomacy are some of the key challenges and opportunities for India.
Understanding India’s historical connections, its present engagements, and the factors that shape its role in the Middle East offers insights into the complex dynamics and evolving nature of India’s relationship with the region.
Key takeaway:
- India’s historical relations with the Middle East: India has had longstanding trade routes and cultural exchanges with the Middle East, shaping its ties with the region.
- India’s past role in the Middle East: India’s non-alignment policy, support for the Palestinian cause, and defense cooperation have played a significant role in shaping the region.
- India’s current engagement in the Middle East: India’s economic and energy partnerships, political and diplomatic relations, and expanding cultural ties showcase its active involvement in the region.
- Geopolitical factors shaping India’s role: Energy security, counter-terrorism cooperation, and navigating regional conflicts are key factors influencing India’s role in the Middle East.
- Challenges and opportunities for India in the Middle East: India faces competition from other players, the challenge of balancing ties with different Middle Eastern states, and the opportunity to leverage soft power and cultural diplomacy.
The Historical Context: India’s Relations with the Middle East

Photo Credits: Thegeopoliticalobserver.Com by Albert Robinson
India’s rich history is intricately woven into the tapestry of the Middle East. In this section, we’ll explore the fascinating historical context of India’s relations with the Middle East. From ancient trade routes and cultural exchanges to the influence of Islamic empires, we’ll uncover the deep connections that have shaped the bond between these regions. Prepare to embark on a journey through time, as we unravel the intertwined past of India and the Middle East.
Ancient Trade Routes and Cultural Exchanges
Ancient trade routes and cultural exchanges have played a significant role in shaping India’s historical relations with the Middle East. The strategic location of ancient India along trade routes connecting the Middle East with East Asia, such as the Silk Road, allowed for the exchange of goods, ideas, and knowledge between the two regions. This led to the establishment of strong cultural and economic ties.
One example of these trade routes is the Silk Road, which facilitated the exchange of various goods, including spices, textiles, and precious metals. This trade route also facilitated cultural interactions and the spread of religions like Buddhism and Hinduism.
The spice trade was another important aspect of these ancient trade routes. Middle Eastern merchants were particularly interested in India’s rich spices, such as pepper, cinnamon, and cardamom. This spice trade not only brought economic prosperity to the regions involved but also introduced new foods and culinary traditions to India.
These exchanges were not limited to trade alone. Scholars, travelers, and missionaries from both India and the Middle East contributed to the exchange of knowledge, art, and architecture. Indian mathematicians, for instance, introduced concepts like algebra and Arabic numerals to the Islamic world, which later spread to Europe.
The influence of language and literature is also noteworthy. Arabic influenced the development of Urdu in India, while Indian literature, including Sanskrit texts like the Vedas and Mahabharata, found an audience in the Middle East. This shared literary heritage has further strengthened the cultural ties between these regions.
Maritime trade played a vital role as well, particularly through India’s coastal regions. These regions served as essential hubs for maritime trade and connected the Middle East with Southeast Asia. Indian traders, sailing across the Arabian Sea, exchanged commodities like textiles, spices, and precious stones. Not only did these maritime connections facilitate cultural interactions, but they also fostered the exchange of ideas through ports like Calicut and Surat.
It is clear that ancient trade routes and cultural exchanges laid the foundation for strong historical ties between India and the Middle East. These exchanges enriched both regions economically and culturally and continue to shape their relations to this day.
India and the Middle East: Where trade routes and cultural exchanges converged, making for some interesting history.
Islamic Empires and India
Islamic Empires and India have a strong historical connection that shaped the Middle East. During the medieval period, Islamic empires like the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Empire ruled over parts of India. These empires had a significant impact on the politics, culture, and religion of the region.
1. The Delhi Sultanate, established in the 13th century, marked the beginning of Islamic rule in India. Founded by Turkish and Afghan invaders, it covered much of northern India. The Sultanate introduced administrative reforms, architectural styles, and Persian literature that influenced Indian society.
2. The Mughal Empire, founded by Babur in the 16th century, was one of the most powerful Islamic empires in Indian history. Under emperors like Akbar, Jahangir, and Shah Jahan, the Mughals expanded their empire across the Indian subcontinent. They brought Persian influences in language, culture, cuisine, and art to India, blending them with indigenous traditions.
3. The Mughals also promoted religious tolerance and a syncretic culture that combined Islamic and Hindu elements. Their architectural masterpieces like the Taj Mahal and Red Fort testify to their grandeur and influence.
4. Trade thrived under Islamic empires, with Middle Eastern merchants establishing extensive commercial networks in India. This led to the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies, benefiting both regions economically and culturally.
5. Islamic empires in India witnessed significant cultural exchanges. Persian and Arabic literature, music, and art flourished, influencing local traditions. Indian poets like Amir Khusro and Bulleh Shah composed works in Persian and embraced Sufi practices, contributing to the rich Sufi tradition in India.
The legacy of Islamic empires in India continues to shape Middle Eastern and Indian relations today. The historical connections and cultural exchanges have created enduring bonds between the two regions. Understanding this shared history is crucial for comprehending the complex dynamics of contemporary Middle Eastern and Indian relations.
India’s journey from curry spice to diplomatic spice in shaping the Middle East.
India’s Role in Shaping the Middle East in the Past
In the realm of geopoltics, India has played a significant role in shaping the Middle East, leaving an indelible mark on its history. As we delve into India’s involvement in the region’s past, we’ll uncover intriguing sub-sections that shed light on India’s non-alignment and Nasserism, its unwavering support for the Palestinian cause, and the crucial aspect of defense and security cooperation. Brace yourself for an eye-opening journey into India’s fascinating impact on the Middle East.
Non-alignment and Nasserism
Non-alignment and Nasserism shaped India’s approach towards the Middle East in the past. India’s policy of non-alignment aimed at maintaining independence from both the Western and Eastern Bloc during the Cold War. This allowed India to have an independent foreign policy, free from alignment with any specific power bloc.
Nasserism, named after Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser, had a strong influence on India’s Middle East strategy. Nasser’s emphasis on Arab nationalism and his anti-colonial stance resonated with India’s own struggle against colonialism. India saw Nasser as a leader fighting for the rights of developing nations and supported his efforts to establish independence and sovereignty in the Arab world.
India’s non-alignment policy and support for Nasserism had various manifestations. India consistently advocated for the rights of Arab states, especially the Palestinian cause. It supported the Arab states’ demand for self-determination and the establishment of a Palestinian state. India also played a role in mediating conflicts in the region, including the Indo-Pakistani war of 1965 and the Arab-Israeli conflict.
India’s non-alignment policy allowed it to maintain diplomatic relations with Middle Eastern countries, regardless of their alliances. This approach helped India maintain cordial relations with both Arab states and Israel, facilitating its engagement in the region.
The policy of non-alignment and support for Nasserism continue to shape India’s Middle East strategy today. India maintains its commitment to the Palestinian cause, supporting a two-state solution and advocating for the rights of the Palestinian people. India’s non-alignment policy enables it to have constructive relationships with countries across the Middle East, allowing it to play a significant role in regional peace and stability.
India’s unwavering support for the Palestinian cause: Making Middle Eastern conflicts even more complicated than your relationship status on Facebook.
India’s Support for Palestinian Cause
India’s support for the Palestinian cause is deeply rooted in its foreign policy objectives in the Middle East. India firmly believes in justice, peace, and the rights of the Palestinian people, which serve as the foundation for its unwavering support. India actively advocates for the establishment of an independent Palestinian state that can coexist harmoniously with Israel. It firmly considers the two-state solution as the most viable option to resolve the longstanding Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
In addition to diplomatic backing, India extends its support through humanitarian aid and development assistance to Palestine. The country plays a significant role in fostering Palestine’s economic growth by constructing schools, hospitals, and housing facilities. India generously offers training opportunities and scholarships to Palestinian students and professionals, empowering them with enhanced skills and knowledge.
India’s support for the Palestinian cause goes beyond mere political alliances; it is deeply rooted in historical and cultural ties with the Middle East. India empathizes with the struggles faced by the oppressed and marginalized, demonstrating its commitment to justice and fairness. India’s support is genuine and unaffected by external pressures or ideological influences. It rests on the recognition of the Palestinians’ legitimate aspirations and their rightful claim to a homeland. India’s unwavering support aligns seamlessly with its broader foreign policy goals of fostering peace, stability, and justice in the region.
India’s solidarity with the Palestinian cause dates back to its early years as an independent nation. Since 1974, India has recognized the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) as the authentic representative of the Palestinian people. Renowned Indian leaders, such as Indira Gandhi and Rajiv Gandhi, have consistently expressed their support for the Palestinian cause. India’s commitment has not wavered despite shifting geopolitical dynamics and international pressures. Actively participating in global forums and initiatives, India strives to find a just and durable solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Its steadfast support is anchored in its unwavering commitment to justice, human rights, and peace in the Middle East. As a responsible global actor, India stands resolute in its support for the Palestinian people, ensuring their pursuit of a secure and prosperous future.
Defense and Security Cooperation
Defense and Security Cooperation in the Middle East shapes India’s relations with the region. This cooperation is driven by mutual interests in maintaining regional stability and addressing common security threats. Here are key aspects of India’s defense and security cooperation in the Middle East:
1. Counter-terrorism collaboration: India actively engages in intelligence sharing, capacity-building, and joint training programs with Middle Eastern countries to counter terrorism. This cooperation aims to prevent extremist ideologies, disrupt terrorist networks, and enhance regional security.
2. Maritime security cooperation: Given its strategic location in the Indian Ocean Region, India collaborates with Middle Eastern states to ensure the security of vital sea lanes and combat piracy and maritime threats. This cooperation includes joint naval exercises, information sharing, and coordinated patrolling efforts.
3. Defense equipment procurement: Middle Eastern countries, including the Gulf states, are important buyers of defense equipment from India. India’s defense industry, under the “Make in India” initiative, is an attractive source for cost-effective and reliable naval vessels, aircraft, and surveillance systems.
4. Joint military exercises: India regularly conducts joint military exercises with Middle Eastern countries to promote interoperability, enhance defense capabilities, and strengthen defense ties. These exercises involve various branches of the armed forces and focus on counter-terrorism, disaster relief, and maritime security.
5. Training and capacity-building: India provides training and support to Middle Eastern countries’ armed forces through exchange programs, courses, and technical assistance. This cooperation aims to enhance the proficiency of armed forces in areas such as counter-terrorism operations, peacekeeping, and disaster response.
India’s defense and security cooperation in the Middle East contributes to regional stability, strengthens bilateral ties, and reinforces India’s commitment to promoting peace and security. The collaboration in these areas builds trust, facilitates intelligence sharing, and enhances the overall security environment in the Middle East.
India’s current engagement in the Middle East: From economic partnerships to political relations and expanding cultural ties, India is strategically navigating the region while keeping its dark sense of humor at bay.
India’s Current Engagement in the Middle East
India’s current engagement in the Middle East is a dynamic force shaping regional dynamics. From economic and energy partnerships to political and diplomatic relations, as well as expanding cultural ties, India’s presence resonates in multiple spheres. As economic powerhouses align and strategic partnerships emerge, it’s crucial to understand India’s evolving role in this complex region. Join us as we navigate through India’s multifaceted engagement in the Middle East, uncovering the significance and impact of its collaboration across diverse sectors.
Economic and Energy Partnerships
Economic and energy partnerships play a crucial role in India’s engagement with the Middle East. These partnerships foster trade, investment, and energy cooperation between India and Middle Eastern countries.
| 1. Trade: | Economic and energy partnerships are instrumental in strengthening the economic ties between India and the Middle East. Bilateral trade has expanded, with both regions benefitting from their complementary economies. The Middle East supplies India with crude oil and natural gas, fulfilling a significant portion of India’s energy needs. In return, India exports pharmaceuticals, textiles, engineering goods, and IT services to the Middle East. |
| 2. Investment: | India and the Middle East have formed strategic investment partnerships to enhance their economic collaboration. The Middle East, particularly the Arab Gulf countries, presents an attractive investment destination for India due to India’s “Make in India” initiative. Middle Eastern countries invest in infrastructure, real estate, technology, and renewable energy in India, thereby boosting both economies. |
| 3. Energy Cooperation: | India’s dependence on Middle Eastern energy resources drives the establishment of robust economic and energy partnerships. The Middle East plays a critical role in meeting India’s energy demands as a major producer of oil and gas. India imports a significant portion of its oil and natural gas from the region. To enhance energy security, India engages in long-term supply agreements and joint ventures with Middle Eastern countries, ensuring a stable energy supply. |
These economic and energy partnerships not only boost trade and investment but also foster diplomatic relationships and cultural exchanges between India and the Middle East. They pave the way for greater cooperation in sectors beyond energy, such as technology, healthcare, education, and tourism.
Pro-tip: Strengthening economic and energy partnerships requires India to diversify its energy sources and expand trade relations with multiple Middle Eastern countries. This reduces dependence on a single region and creates opportunities for collaboration, ensuring a more sustainable and resilient economic relationship.
India’s political and diplomatic relations in the Middle East – where making friends and influencing nations is a delicate dance filled with more twists and turns than a Bollywood movie.
Political and Diplomatic Relations
Political and diplomatic relations are crucial to India’s engagement with the Middle East. India has maintained longstanding relationships with countries in the region, with deep historical roots.
1. Effective diplomacy: India actively pursues diplomatic ties to enhance political cooperation. This involves exchanging high-level visits, promoting dialogue, and forging strategic partnerships. For example, Prime Minister Narendra Modi has made multiple visits to the Middle East to strengthen political ties.
2. Strategic partnerships: India has established strategic partnerships with the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and Israel. These partnerships focus on defense and security cooperation, intelligence-sharing, and counter-terrorism efforts. They contribute to regional stability and combat common security challenges.
3. Peacebuilding and conflict resolution: India promotes peace and stability in the Middle East. It consistently supports the Palestinian cause and advocates for a peaceful resolution to the Arab-Israeli conflict. India’s diplomatic efforts aim to foster dialogue and understanding among conflicting parties, contributing to regional peace.
4. Economic cooperation: Political and diplomatic relations have paved the way for robust economic partnerships between India and Middle Eastern countries. Both regions are important trading partners, with significant bilateral trade in sectors like oil, gas, and investments. Economic ties foster mutual prosperity and contribute to the growth and development of both economies.
5. Cultural exchanges: Political and diplomatic relations facilitate cultural interactions and people-to-people exchanges between India and the Middle East. These exchanges foster cultural understanding, promote tourism, and strengthen the bonds of friendship between nations. India’s rich cultural heritage is showcased through cultural festivals, exhibitions, and events in Middle Eastern countries.
India’s political and diplomatic relations in the Middle East are shaped by its foreign policy objectives, security aspirations, and economic interests. These relations play a pivotal role in enhancing regional stability, promoting peace, and fostering cooperation. As India navigates the geopolitical complexities of the region, strong political and diplomatic ties remain essential for its strategic significance as a global player.
Expanding Cultural Ties
Expanding cultural ties between India and the Middle East foster mutual understanding, respect, and cooperation. Cultural exchanges enhance people-to-people connections, promote tourism, and strengthen diplomatic relations. These expanding cultural ties between India and the Middle East enrich the cultural fabric of both regions and contribute to economic growth, social harmony, and diplomatic ties. These cultural exchanges build stronger bilateral relationships, fostering a deeper understanding of customs, traditions, and values.
1. Cultural exchange programs: India and the Middle Eastern countries actively engage in art exhibitions, music festivals, dance performances, and film screenings as a part of expanding cultural ties. Sharing cultural heritage allows appreciation and learning from each other’s traditions.
2. Educational collaborations: Universities and educational institutions in India and the Middle East collaborate on student exchange programs, joint research endeavors, and faculty interactions, contributing to expanding cultural ties. This widens students’ perspectives, develops cross-cultural skills, and forges lasting friendships.
3. Language learning: Indian languages like Hindi, Urdu, and Malayalam are widely spoken in the Middle East, further promoting expanding cultural ties. Similarly, learning Arabic and other regional languages in India is gaining popularity. Language learning programs and institutes bridge the communication gap and facilitate cultural understanding.
4. Promotion of cuisine and traditional arts: Indian food, known for its variety of flavors and spices, is popular in the Middle East, thus playing a significant role in expanding cultural ties. Indian restaurants can be found in almost every Middle Eastern country, serving authentic cuisine. At the same time, traditional Middle Eastern arts like calligraphy and carpet weaving are gaining recognition in India, fostering cultural appreciation.
5. Cultural diplomacy: Festivals and events celebrate both Indian and Middle Eastern cultures to promote cultural diplomacy and contribute to expanding cultural ties. These events showcase music, dance, theater, literature, and visual arts, providing a platform for collaboration and talent sharing.
Pro-tip: To further expand cultural ties, encourage people-to-people interactions, support cultural institutions and initiatives, and provide platforms for artists, scholars, and students to collaborate and exchange ideas. Nurturing cultural ties helps build bridges of understanding and resilience in an interconnected world.
From energy security to counter-terrorism cooperation, India dances through geopolitical landmines in the Middle East.
The Geopolitical Factors Shaping India’s Role
India’s role in shaping the Middle East goes beyond mere involvement; it is a result of various geopolitical factors that have influenced its actions in the region. From ensuring energy security to fostering counter-terrorism cooperation and navigating regional conflicts, India’s engagements in the Middle East are driven by multifaceted motivations. In this section, we will explore these different factors that have shaped India’s strategic decisions, offering insights into its complex role within this dynamic region.
Energy Security
Energy Security
When it comes to energy security, India faces challenges and opportunities. Here are key factors to consider:
1. Diversification of energy sources: India should diversify its energy sources to reduce dependence on any single country or region. Exploring renewable energy options like solar and wind power can enhance energy security and reduce vulnerability to supply disruptions.
2. Energy infrastructure development: Building robust energy infrastructure is crucial for reliable and uninterrupted energy supply. This includes expanding and modernizing transmission and distribution networks, investing in storage facilities, and improving energy transportation efficiency.
3. Promoting domestic production: Increasing domestic production of energy resources, including oil, gas, and coal, can help reduce India’s reliance on imports. Initiatives like the “Make in India” program encourage indigenous industries and support domestic energy production growth.
4. Enhancing regional cooperation: Collaborating with neighboring countries and fostering regional energy cooperation can contribute to India’s energy security. Joint energy projects, such as cross-border pipelines or power grids, can ensure a reliable and diverse energy supply, benefiting all participating nations.
5. Efficiency and conservation: Improving energy efficiency and promoting conservation practices reduce energy demand and enhance energy security. Implementing energy-efficient technologies, promoting energy-saving practices in industries and households, and investing in sustainable energy research and development are important steps in this direction.
In recent years, India has made significant progress in its energy security efforts. One notable example is the success of the Ujjwala Yojana, a scheme aimed at providing clean cooking fuel to households. Through this initiative, India has distributed over 80 million LPG connections to low-income households, ensuring access to clean and reliable cooking fuel. This improves the health and well-being of millions of people and enhances energy security by reducing reliance on traditional biomass fuels.
India and the Middle East: Joining forces to fight terrorism and ensure a brighter future.
Counter-terrorism Cooperation
Counter-terrorism cooperation plays a crucial role in India’s engagements with the Middle East. India actively collaborates with Middle Eastern countries in sharing intelligence and conducting joint operations to counter terrorism.
These collaborations effectively disrupt terrorist networks and prevent attacks. India also signs bilateral and multilateral agreements with Middle Eastern countries to enhance cooperation in counter-terrorism, including intelligence-sharing, capacity-building, and the exchange of best practices.
India consistently advocates for greater international cooperation in counter-terrorism efforts, participating in global forums such as the United Nations and the Global Counterterrorism Forum. India supports Middle Eastern countries in their efforts to combat terrorism and extremism within their borders through training and capacity-building assistance, information sharing, and coordination.
It is vital for India’s national security interests to have counter-terrorism cooperation with Middle Eastern countries due to concerns about terrorism emanating from the region, particularly from Pakistan-based terrorist groups. India’s focus on counter-terrorism cooperation is driven by its commitment to global peace and stability.
India recognizes that terrorism is a global challenge that requires collective action and cooperation among nations. By actively engaging in counter-terrorism efforts, India aims to contribute to a safer and more secure world. Going forward, India will continue to prioritize counter-terrorism cooperation in its foreign policy objectives to address emerging challenges and develop comprehensive strategies to counter radicalization and extremism.
Counter-terrorism cooperation between India and the Middle East is a key aspect of their bilateral relations.
Navigating Regional Conflicts
Navigating regional conflicts in the Middle East is crucial for India’s foreign policy objectives. India actively engages in diplomatic efforts to resolve conflicts in the region. India believes in peaceful resolutions and advocates for dialogue and negotiations to navigate these regional conflicts.
India’s approach to navigating regional conflicts is based on principles of non-interference, respect for sovereignty, and respecting the aspirations of the countries involved. India understands the complex dynamics and sensitivities of the region and aims to maintain good relations with all parties while navigating these conflicts.
India has played a constructive role in various conflicts, such as the Israeli-Palestinian issue, Yemen, and the Syrian crisis. In the Israeli-Palestinian issue, India supports a two-state solution and the right of the Palestinian people to self-determination. India provides humanitarian assistance to countries affected by conflicts, including Yemen and Syria, as part of its navigation of regional conflicts.
India’s ties with the Middle East, including historical, cultural, and economic connections, greatly influence its ability to navigate regional conflicts. These ties provide India with a platform to engage with regional actors and promote peaceful resolutions, thus effectively navigating these conflicts.
Despite challenges, navigating regional conflicts in the Middle East presents opportunities for India to enhance its role as a global player. By actively participating in conflict resolution processes, India can strengthen strategic partnerships and promote stability and peace in the region, further enhancing its navigation of these regional conflicts.
Challenges and Opportunities for India in the Middle East
India’s journey in shaping the Middle East has been riddled with challenges and brimming with opportunities. From facing fierce competition from other players to carefully balancing ties with different Middle Eastern states, India has navigated the complex landscape with finesse. In this section, we will explore how India harnesses the power of soft diplomacy and cultural ties to leverage its influence in the region. Join us as we delve into the dynamic world of India’s role in the Middle East, discovering the challenges and opportunities it encounters along the way.
Competition from Other Players
Competition from other players significantly shapes India’s role in the Middle East. In the economic realm, India finds itself in fierce competition with China and the United States. The Belt and Road Initiative and investments made by China in the Arab Gulf pose a challenge to India’s strategic investments. At the same time, the United States forges stronger economic ties with crucial trading partners of India, such as Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates.
When it comes to strategic and security considerations, India must navigate the competitive dynamics between Saudi Arabia and Iran. Both countries wield a considerable amount of influence in the Middle East and actively seek strategic partnerships. India, however, maintains a balanced approach by refraining from taking sides in regional conflicts. Nevertheless, the competition between Saudi Arabia and Iran adds a layer of complexity to India’s position.
Competing in cultural and diplomatic engagements is also part of India’s reality. The United Arab Emirates and Qatar have made substantial investments in promoting their cultural and soft power influence in the region. In response, India has taken steps to enhance its own cultural diplomacy efforts in the Middle East, in order to keep up with this competition.
Balancing ties with different Middle Eastern states is like juggling kebabs and falafels – a delicate art that requires skill, finesse, and a dash of tahini.
Balancing Ties with Different Middle Eastern States
Balancing ties with different Middle Eastern states is a fundamental aspect of India’s foreign policy objectives in the region. India acknowledges the strategic significance of maintaining relationships with multiple countries in the Middle East to protect its national interests and promote regional stability.
India’s strategy for achieving a balance in ties encompasses various dimensions, including political, economic, and security cooperation. India aims to strengthen its economic relations with Middle Eastern states through trade, investment, and joint ventures. An excellent example of this is the United Arab Emirates, which has emerged as a crucial investment destination for India, with bilateral trade amounting to billions of dollars annually.
India actively engages in political and diplomatic relations with Middle Eastern states to nurture mutual understanding and collaboration. Frequent high-level visits and diplomatic engagements contribute significantly to building trust and enhancing cooperation in areas of shared interest, such as energy security, counter-terrorism, and regional stability.
India endeavors to expand cultural ties with Middle Eastern states, recognizing the value of people-to-people exchanges in building enduring relationships. Programs promoting cultural interchange, academic exchanges, and tourism initiatives play a pivotal role in fostering greater understanding and cooperation.
Balancing ties with different Middle Eastern states is indispensable for navigating the complexities and diversities of the region. India strives to strengthen its strategic partnerships by taking into account the specific interests and priorities of each country while maintaining a balanced approach and respecting the sovereignty of Middle Eastern states. This approach allows India to forge mutually beneficial relationships while safeguarding its national interests.
Leveraging Soft Power and Cultural Diplomacy
Leveraging Soft Power and Cultural Diplomacy is crucial to India’s foreign policy strategy in the Middle East. India recognizes the power of culture, arts, and education in building relationships and promoting understanding. Active use of soft power tools, such as cultural exchanges, language education, and promoting Indian cinema and music, enhances India’s influence in the region.
India actively engages in cultural diplomacy by organizing festivals, exhibitions, and film festivals with Middle Eastern countries. These initiatives showcase India’s cultural heritage and foster dialogue and exchanges. By promoting dance, music, and traditional arts, India strengthens its presence and creates a positive image.
Language education is also valuable in India’s soft power diplomacy. The establishment of cultural centers and language institutes in Middle Eastern nations enables people to learn Indian languages, fostering better communication.
Indian cinema, known as Bollywood, is popular in the Middle East. Bollywood movies are screened in local theaters and Indian actors have a considerable fan following. This cultural influence bridges the gap between India and the Middle East, fostering understanding and connections.
Education is essential in cultural diplomacy. India offers scholarships to Middle Eastern students, creating opportunities for cross-cultural interactions and building relationships. These educational exchanges contribute to the growth of both regions.
India’s emphasis on leveraging soft power and cultural diplomacy in the Middle East highlights its commitment to nurturing relationships based on respect and understanding. By actively engaging in cultural exchanges and promoting its cultural heritage, India cements its presence and influence in the region.
Some Facts About India’s Role in Shaping the Middle East: Past and Present:
- ✅ India now considers the United States, Israel, and the Arab Gulf as important partners in the Middle East.
- ✅ India’s growing dependence on Middle Eastern energy has increased the strategic significance of its relationship with the region.
- ✅ India’s security aspirations are expanding, particularly in the Indian Ocean region, and security ties with Middle Eastern states are seen as important in achieving these aspirations.
- ✅ India is concerned about increasing instability and the weakening of states in the Middle East, which threaten its energy imports and diaspora.
- ✅ India’s inclusion in the Middle East Quad, a new joint working group with the United States, Israel, and the United Arab Emirates, reflects a shift in India’s foreign policy in the region.
###Reference Data (Source: Our Team):
Source: https://www.csis.org/analysis/indias-middle-east-strategy India’s Middle East strategy has evolved over time. In the past, India supported the Palestinians against Israel and had no strategic relationship with the Gulf. Today India takes a more strategic view of the Middle East. Three important changes have occurred: India now considers the United States, Israel, and the Arab Gulf as important partners. The United States is one of India’s best friends in the region, Israel is a major partner in defense and security issues, and Saudi Arabia and the UAE are important partners. India has three broad objectives in the Middle East: drawing Gulf capital into its economy, partnering with moderate Islamic countries to counter radical ideologies, and building security cooperation. India is not yet a major power but aims to engage more in the security politics of the Middle East. China’s role in the region is a concern for India, as it wants the United States to remain the security guarantor of the Gulf. India sees itself as a medium power and prefers to build partnerships rather than compete with other major powers. The I2U2 partnership between India, Israel, the United States, and the UAE focuses on economic projects but could eventually develop security cooperation. India is aware of the sensitivities surrounding its Muslim minority and takes steps to prevent their marginalization. Prime Minister Modi has built strong relations with the Gulf and is conscious of the role of Islam in South Asia. India’s relationship with the Middle East is now interest-based rather than driven by ideology. India has also engaged with Iran and aims to continue its robust relations despite US sanctions.
Source: https://www.brookings.edu/articles/indias-shifting-role-in-the-middle-east/ India’s role in the Middle East is evolving from being primarily focused on economic ties to becoming more strategically engaged. In the past, India mainly focused on exporting labor and importing oil from the region. In recent years, several factors have raised the strategic stakes for India. India’s growing dependence on Middle Eastern energy has increased the strategic significance of its relationship with the region. India’s net oil imports as a percentage of demand have grown significantly, and over half of its oil and gas now comes from the Gulf. This has led to efforts to transform the buyer-seller relationship into a deeper strategic partnership, as seen in the joint statement during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Saudi Arabia. India is making strategic investments in Iran, particularly in the Chabahar Port. India’s security aspirations are expanding, particularly in the Indian Ocean region. Indians believe that their country should have the most powerful navy in the Indian Ocean and should lead cooperation in the region. Security ties with Middle Eastern states are seen as important in achieving these aspirations, as they help protect sea lanes and secure choke points. Indian policymakers are concerned about increasing instability and the weakening of states in the Middle East, which threaten Indian energy imports and diaspora. India’s past inability to influence geopolitics in the region has led to costly evacuations of its diaspora, including the largest evacuation in history during the Gulf War. The decline of American influence in the Middle East and the rise of non-Western powers like China have further increased the strategic relevance of the region for India. China’s growing economic relationship with the Middle East and its strategic ties with regional powers pose a challenge for India’s energy security and influence. In response, India has been increasing its engagement with the Middle East through bilateral visits, security and defense agreements, and positioning itself between the West and Russia in regards to the Syrian conflict. India’s evolving role in the Middle East reflects its growing strategic interests and aspirations in the region. As the United States considers its strategic options in the changing Middle East, India’s increasing role may become impossible to ignore. Source: https://foreignpolicy.com/2021/10/29/india-modi-middle-east-quad-israel-uae-geopolitics/ India has joined the United States, Israel, and the United Arab Emirates in a new joint working group to coordinate strategy in the Middle East. This new grouping, often referred to as the Middle East Quad, is similar to the Indo-Pacific Quad that includes the United States, India, Australia, and Japan. While the Middle East Quad is still in its early stages and lacks the intensity of its eastern counterpart, it aims to leverage the overlapping interests of the four countries in energy, climate, trade, and regional security. India’s inclusion in this group is significant as it reflects a shift in India’s foreign policy in the Middle East. Historically, India has kept its distance from the United States, Israel, and the Persian Gulf states on regional issues. Under Prime Minister Narendra Modi, India has developed closer ties with Israel and the UAE, which has led to its inclusion in this new partnership. This partnership with the United States and its regional allies aligns with India’s widening foreign-policy footprint and its willingness to work with these countries to stabilize both the Middle East and East Asia. India’s role in the Middle East is also a reflection of its historic position in the region. In the colonial era, India played a key role in the British domination of the Indian Ocean and adjacent areas. It provided military resources and helped stabilize large parts of Asia. India’s return to the Middle East as an independent actor with its own political agency is a reestablishment of those historic connections. India’s foreign policy in the Middle East has evolved over time. In the past, India distanced itself from the region’s security politics and abandoned its role in the Indian Ocean’s economic globalization. Recent shifts in India’s foreign policy, including its embrace of Israel and engagement with the UAE and Saudi Arabia, have allowed for greater pragmatism and a more prominent role in the Middle East. The initial focus of the Middle East Quad will be on economic issues, but it could lead to greater strategic coordination among the four partners in the region. The Middle East Quad is part of the effort to rearrange the regional order and balance of power, with India reclaiming its geographic, economic, and political interests in the region. Source: https://asiasociety.org/asias-new-pivot/india India’s relations with the Middle East, particularly the Gulf and West Asia, have undergone significant changes in recent years. Indian policymakers now view the region strategically, while Middle Eastern countries see India as an appealing partner due to concerns about US commitment and the need to diversify their markets. This has led to increased engagement between India and Middle Eastern countries on a wide range of topics. The ties between India and the Middle East have a long history, dating back to ancient trade routes and the British Raj. In recent years, both sides have sought to transcend historical constraints and forge stronger relations. Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi has played a central role in this shift, driven by his foreign policy objectives of positioning India as a global player and boosting economic development. Economic and energy ties are a key aspect of India’s relations with the Middle East. India is highly dependent on the region for its energy needs, with a significant portion of its oil imports coming from the Middle East. India’s growing energy demand is projected to continue, making the Middle East essential for its long-term economic viability. India has also invested in expanding its domestic refining capacity and has become a major exporter of refined oil. Middle Eastern countries, particularly Saudi Arabia and the UAE, have shown interest in investing in India’s energy sector. Saudi Aramco and ADNOC have agreed to jointly develop a refinery in India, while Saudi Arabia and the UAE have made significant investment pledges in various sectors. India is also seeking investment from the UAE to help diversify its economy. Trade relations between India and the Middle East have grown and diversified, with India exporting a range of products to the region. The UAE is India’s top market in the Middle East, particularly for exports of refined oil and precious gems. India has no formal trade agreements with Middle Eastern countries. India has also ramped up its diplomatic engagement with the Middle East, signing strategic partnerships with Iran, Oman, and Saudi Arabia. Modi has prioritized relations with the UAE and Israel, viewing them as key strategic partners. India has also maintained its engagement with Iran, despite growing ties with Israel. India’s relations with the Middle East are evolving and becoming more multifaceted, encompassing economic, energy, strategic, and diplomatic aspects. Both India and Middle Eastern countries see mutual benefits in deepening
Frequently Asked Questions
What is India’s role in shaping the Middle East during World War II?
India’s role in shaping the Middle East during World War II was primarily driven by its strategic location as a British colony. Acting as a reliable base for British military operations, India provided military and logistical support to stabilize large parts of Asia. India’s return to the Middle East as an independent actor reflects a reestablishment of those historic connections.
How has India’s Middle East strategy evolved over time?
India’s Middle East strategy has evolved from supporting the Palestinians against Israel and having no strategic relationship with the Gulf to viewing the United States, Israel, and the Arab Gulf as important partners. India now considers the United States as one of its best friends in the region, partners with Israel on defense and security issues, and sees Saudi Arabia and the UAE as important partners. Its relationship with the Middle East is now interest-based rather than driven by ideology.
What are India’s objectives in the Middle East?
India has three broad objectives in the Middle East: drawing Gulf capital into its economy, partnering with moderate Islamic countries to counter radical ideologies, and building security cooperation. India aims to engage more in the security politics of the Middle East and wants the United States to remain the security guarantor of the Gulf. India sees itself as a medium power and prefers to build partnerships rather than compete with other major powers.
What are the key factors that have raised the strategic stakes for India in the Middle East?
Several factors have raised the strategic stakes for India in the Middle East. India’s growing dependence on Middle Eastern energy has increased the strategic significance of its relationship with the region. India’s net oil imports as a percentage of demand have grown significantly, and over half of its oil and gas now comes from the Gulf. India’s security aspirations are expanding, particularly in the Indian Ocean region. Indian policymakers are concerned about increasing instability and the weakening of states in the Middle East, which threaten Indian energy imports and diaspora. The decline of American influence in the Middle East and the rise of non-Western powers like China have further increased the strategic relevance of the region for India.
What is the significance of India’s inclusion in the Middle East Quad?
India’s inclusion in the Middle East Quad, a joint working group with the United States, Israel, and the United Arab Emirates, reflects a shift in India’s foreign policy in the Middle East. Historically, India maintained some distance from these countries on regional issues. Under Prime Minister Narendra Modi, India has developed closer ties with Israel and the UAE, leading to its inclusion in this new partnership. The Middle East Quad aims to leverage the overlapping interests of the four countries in energy, climate, trade, and regional security.
What are the key aspects of India’s relations with the Middle East?
India’s relations with the Middle East encompass economic, energy, strategic, and diplomatic aspects. Economically, India is highly dependent on the region for its energy needs and has invested in expanding its domestic refining capacity. Energy and trade ties have grown and diversified, with the UAE being India’s top market in the Middle East. India has also prioritized strategic partnerships with Middle Eastern countries like Iran, Oman, and Saudi Arabia. Diplomatically, Prime Minister Modi has played a central role in enhancing India’s relations in the region, viewing Israel and the UAE as key strategic partners. Both India and Middle Eastern countries see mutual benefits in deepening their commercial and strategic relationship.