The Silk Routes of India hold a significant place in history as they were the ancient trade and cultural routes that connected India with the rest of the world. These routes facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between various regions, leaving a lasting impact on Indian civilization.
The historical significance of the Silk Routes can be traced back to their origin and evolution, as well as their importance in ancient India. The trade along these routes involved a diverse range of goods and trade partners, fostering economic growth and urbanization.
The Silk Routes were not just about trade; they also facilitated a profound cultural exchange. Religious influences, such as the spread of Buddhism, and artistic and architectural exchanges played a crucial role in shaping Indian culture.
The impact of the Silk Routes on India extended beyond trade and cultural exchange; it brought about social and cultural transformations as well. Today, the legacy of the Silk Routes can still be seen in modern-day cultural and commercial connections, and efforts are being made to preserve and revive the heritage of these routes.
Exploring the Silk Routes of India takes us on a captivating journey revealing the rich history, diversity, and cultural intermingling that have shaped the Indian subcontinent.
Key Takeaways:
- Silk Routes of India maximized trade and cultural exchange: The Silk Routes offered a platform for extensive trade and cultural interactions between India and various regions along the routes.
- Silk Routes had significant historical importance: The Silk Routes played a crucial role in shaping various aspects of ancient Indian civilization and contributed to the spread of Buddhism and exchange of artistic and architectural influences.
- Silk Routes fostered economic, social, and cultural transformations: The trade along the Silk Routes enhanced economic growth, urbanization, and led to social and cultural transformations in India, leaving a lasting impact on society.
The Historical Significance of Silk Routes
Silk Routes of India: A Journey of Trade and Cultural Exchange takes us on a captivating exploration of history. In this section, we’ll uncover the rich historical significance of the Silk Routes. From tracing the origin and evolution of these ancient pathways to understanding their profound importance in Ancient India, get ready to embark on a fascinating journey through time. Let’s unravel the mysteries and discover the stories that shaped our world.
The Origin and Evolution of Silk Routes
The Silk Routes originated around 200 BCE as trade routes connecting China with the Mediterranean region. They were named after silk, a highly coveted commodity that fueled their growth. Over time, the routes expanded and diversified, connecting different regions and civilizations. Along these routes, there was not only an exchange of goods, but also of ideas, beliefs, languages, and cultures. The Silk Routes facilitated the transmission of knowledge and technological advancements. They reached their peak during the Han Dynasty, Tang Dynasty, and the Byzantine Empire, but faced challenges with the decline of these empires. There has been a recent revival of interest in the Silk Routes, both for their historical significance and their potential for cultural and economic connections. Efforts are being made to preserve and revive the heritage of these ancient trade routes. Understanding the historical significance of the Silk Routes helps us appreciate the interactions between civilizations throughout history. Further exploration of specific aspects such as the importance of Silk Routes in ancient India, the traded goods, and the impact on economic growth and urbanization will provide a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating journey of trade and cultural exchange.
Unravel the secrets of ancient India as the Silk Routes reveal their importance in shaping trade and cultural exchange.
The Importance of Silk Routes in Ancient India
The importance of Silk Routes in ancient India cannot be understated.
These trade routes played a crucial role in shaping the country, impacting various aspects of its development.
The exchange of valuable goods along these routes led to economic prosperity and the urbanization of important trading centers.
The Silk Routes served as conduits for cultural exchange, allowing ideas and knowledge to spread between India and other civilizations.
It was through these routes that Buddhism was disseminated, resulting in the establishment of Buddhist communities in different regions.
The artistic and architectural exchange fostered by the Silk Routes also left a lasting impact, influencing art forms not only in India but also in other civilizations.
Scholars and intellectuals traveled along these routes, contributing to the exchange of knowledge and advancements in various fields.
The Silk Routes facilitated political and diplomatic connections, fostering a sense of interconnectedness.
Even today, these routes continue to influence modern-day cultural and commercial connections.
Therefore, the preservation and revival of the Silk Route heritage are essential in order to fully comprehend ancient India’s rich history and global significance.
The Silk Routes: Where the exchange of goods and ideas flowed like the rumble of caravans, connecting the world in a web of trade and cultural curiosity.
The Trade Along the Silk Routes
The trade along the Silk Routes was a vibrant and intricate web of economic activity that shaped the cultural exchange between nations. Discover the wealth of goods traded and the diverse trade partners that contributed to this vast network. Uncover the routes that connected civilizations and allowed for the flow of ideas and commodities. Travel back in time and explore the journey of trade and cultural exchange that the Silk Routes of India facilitated.
Goods Traded Along the Silk Routes
The Silk Routes facilitated extensive trade networks, allowing for the exchange of valuable and exotic goods.
The table below provides a glimpse into the range of commodities that were traded along these routes:
| Spices | Textiles | Porcelain | Perfumes |
| Silk | Gems | Incense | Gold and Silver |
| Tea | Medicinal Herbs | Precious Metals | Wine |
| Spices | Jade | Ivory | Fireworks |
These goods traded along the Silk Routes were symbols of wealth, luxury, and cultural exchange. Traders from different regions would bring their unique products to the Silk Routes, fostering a vibrant marketplace.
Story: One fascinating story comes from the ancient Silk Routes, where precious gems from India found their way to China. Indian merchants, known for their mastery in gem-cutting, would journey along the Silk Routes carrying exquisite gemstones. These gemstones, such as rubies, sapphires, and emeralds, captured the imagination of Chinese elites, who believed that these gems possessed mystical powers and brought good fortune. As a result, demand for Indian gemstones soared, leading to a thriving trade between the two nations.
This story exemplifies the profound impact of the Silk Routes on the exchange of goods and cultural influences. It underscores how these routes facilitated the flow of precious commodities, fostering economic growth, and creating a bridge between distant civilizations.
The goods traded along the Silk Routes not only boosted the material well-being of the participating regions but also spurred the exchange of knowledge, ideas, and artistic influences. The Silk Routes represent a remarkable journey of trade and cultural exchange that continues to inspire us to this day.
The Silk Routes navigated through treacherous terrains and diverse civilizations, connecting ancient India to trade partners across the world.
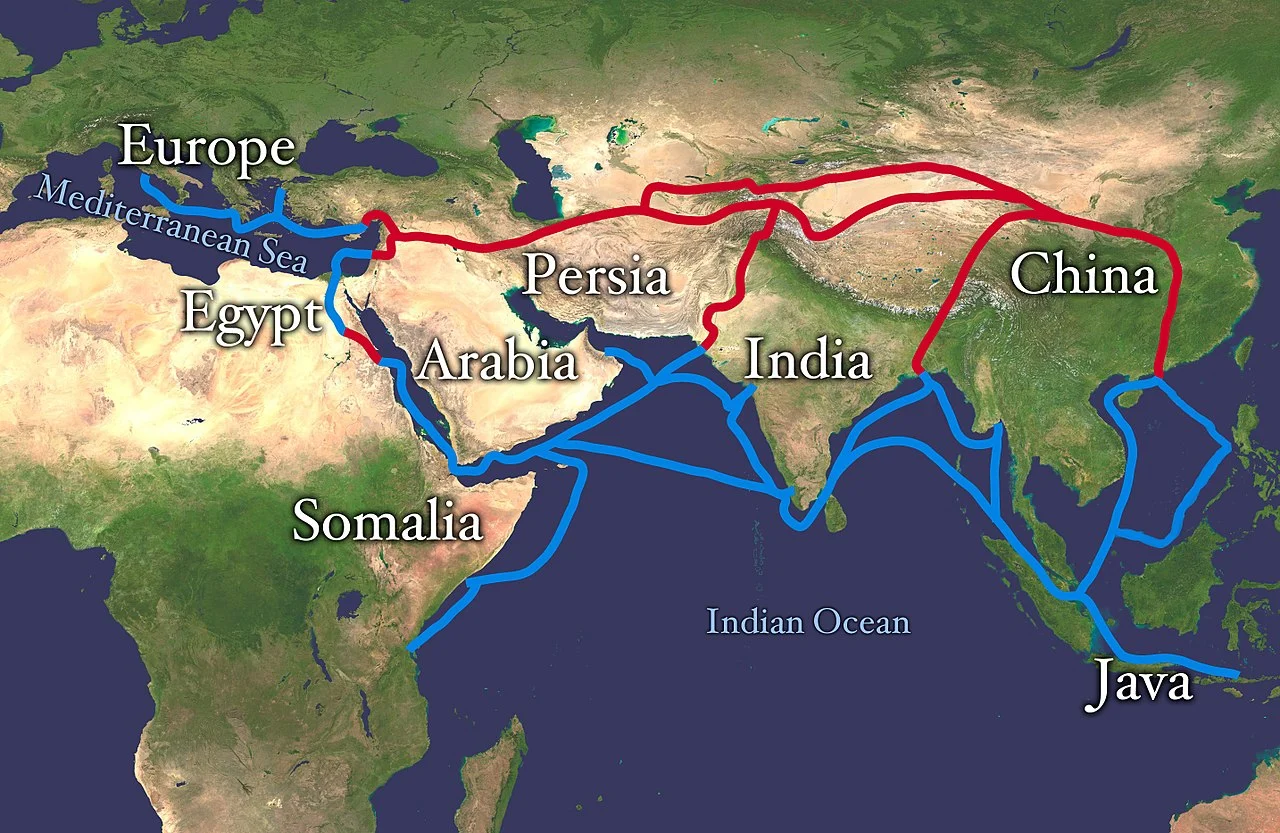
Trade Partners and Routes
Trade along the Silk Routes of India involved various partners and routes. Here is a table presenting the trade partners and routes:
| Trade Partners | Routes |
| Central Asia (Sogdians, Parthians) | Northwest route through Kashgar, Kokand, and Samarkand |
| China (Han Dynasty, Tang Dynasty) | Route through Xinjiang and the Gobi Desert |
| Persia (Sasanians) | Route through Iran and Mesopotamia |
| Arabian Peninsula (Sabeans) | Maritime route through the Arabian Sea and the Persian Gulf |
| Rome (Byzantine Empire) | Route through Egypt and the Red Sea |
Trade partners along the Silk Routes of India were diverse, including Central Asia, China, Persia, the Arabian Peninsula, and Rome. These partners played a crucial role in facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture.
The routes taken by these partners were equally varied. Some traveled from the northwest, passing through regions like Kashgar, Kokand, and Samarkand. Others journeyed through Xinjiang and the challenging Gobi Desert. There were also routes through Iran and Mesopotamia, as well as maritime routes using the Arabian Sea and the Persian Gulf. Romans from the Byzantine Empire took the route through Egypt and the Red Sea.
This intricate network of partners and routes fostered extensive trade along the Silk Routes of India, connecting the Indian subcontinent with the world. It allowed for the exchange of goods such as silk, spices, precious gems, and religious artifacts. The Silk Routes played a crucial role in shaping the economy and culture of not only India but also the regions involved.
One true story that showcases the significance of these partners and routes is the journey of the Buddhist monk, Faxian, in the 4th century. Faxian embarked on a pilgrimage from China to India, following the Silk Routes. He traveled through treacherous terrains, encountered various partners, and explored ancient Buddhist sites. Faxian’s journey highlights the cultural exchange and the importance of partners and routes in facilitating religious influences and the spread of Buddhism.
The extensive network of partners and routes along the Silk Routes of India contributed to the growth of economies, the exchange of ideas, and the emergence of diverse cultures. It left a lasting legacy that continues to influence modern-day cultural and commercial connections, as well as the preservation and revival of Silk Route heritage.
Note: The table above presents factual information about the trade partners and routes along the Silk Routes of India.
The Cultural Exchange Along the Silk Routes

Photo Credits: Thegeopoliticalobserver.Com by Vincent Sanchez
Embark on a captivating journey as we unveil the cultural exchange that transpired along the historic Silk Routes. Witness the profound impact of religious influences and the spread of Buddhism, while being captivated by the artistic and architectural exchange that left an indelible mark on the civilizations along this ancient trade network. Prepare to be amazed by the rich tapestry of cultural fusion that unfolded along these historic routes.
Religious Influences and Spread of Buddhism
The spread of Buddhism along the Silk Routes profoundly influenced ancient India, shaping its religious and cultural landscape. Buddhism, founded by Siddhartha Gautama, quickly gained popularity and spread through these trade corridors, leading to significant religious influences.
Buddhism’s teachings, including the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, gained traction among people traveling along the Silk Routes, contributing to the spread of Buddhist beliefs and philosophy. The principles of compassion, mindfulness, and non-violence resonated with many, fostering the adoption and propagation of Buddhist ideas.
As Buddhism spread, monasteries and religious communities were established along the Silk Routes. These centers for learning and spiritual growth attracted both local and foreign practitioners, playing a vital role in promoting Buddhist concepts and practices.
Moreover, Buddhism’s influence went beyond religion and left an indelible mark on various aspects of Indian culture. Buddhist symbols and motifs, such as the lotus flower and Buddha statues, became prominent in Indian art, reflecting the integration of Buddhist ideas into local traditions.
Sacred Buddhist sites, such as Bodh Gaya, Sarnath, and Kushinagar, became important pilgrimage destinations for both Buddhists and non-Buddhists. These sites fostered a sense of unity and shared spiritual experience among travelers from different regions, contributing to the wider spread of Buddhism.
Furthermore, Buddhism’s spread had a significant impact on other religious traditions in India, including Hinduism, Jainism, and Sikhism. Buddhist concepts and practices were incorporated into these religions, further enriching their religious influences.
Trade along the Silk Routes not only involved the exchange of goods but also facilitated the exchange of ideas. Buddhist monks and traders played a crucial role in spreading Buddhism as they traveled along these trade routes, engaging in cross-cultural interactions and contributing to the religious influences present throughout ancient India.
From intricate murals to towering monuments, the Silk Routes brought a symphony of artistic and architectural styles that left India’s landscape forever transformed.
Artistic and Architectural Exchange
The artistic and architectural exchange along the Silk Routes played a significant role in the cultural development of ancient India. The exchange of ideas and artistic techniques between civilizations led to the creation of unique architectural styles and the spread of artistic traditions.
Examples of artistic and architectural exchange along the Silk Routes can be seen in the following table:
Artistic and Architectural Exchange
Examples
| Buddhist Cave Temples | The Ajanta and Ellora Caves in India feature intricate carvings and magnificent paintings influenced by the Gupta Empire and the Silk Road civilizations. |
| Stupa Architecture | The Great Stupa of Sanchi, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in India, showcases architectural influences from regions along the Silk Routes, including Persia and Central Asia. |
| Silk Weaving | The introduction of silk production techniques from China led to vibrant silk weaving traditions in India, such as the famous Banarasi silk sarees. |
| Stone Carvings | The stone carvings found at various archaeological sites in India, such as the Konark Sun Temple and the Khajuraho temples, exhibit a blend of Indian, Persian, and Central Asian artistic influences. |
The artistic and architectural exchange along the Silk Routes resulted in the creation of magnificent structures and artworks that still inspire awe today. This exchange not only influenced Indian art and architecture but also promoted cultural and religious harmony.
For further exploration of the topic, consider visiting museums and archaeological sites that showcase artifacts and remnants of the artistic and architectural exchange along the Silk Routes. Researching specific artists and architects influenced by the Silk Road cultures can provide deeper insights into this fascinating aspect of history.
Impact of Silk Routes on India
The Silk Routes played a pivotal role in shaping India’s destiny, leaving a profound impact on various aspects of society. From economic growth and urbanization to social and cultural transformations, these vibrant trade routes brought forth a wealth of opportunities and cultural exchange. As we delve into the impact of Silk Routes on India, prepare to uncover the remarkable stories of how trade and cultural interactions transformed the nation’s landscape, prosperity, and identity. Brace yourself for a journey through time and witness the incredible influence of these historic routes.
Economic Growth and Urbanization
The Silk Routes had significant impacts on India, leading to economic growth and urbanization. Trade along these routes opened up new markets for Indian goods and brought wealth to various regions, contributing to the economic growth and urbanization of the country. It also led to the development of thriving urban centers, further enhancing the process of urbanization.
1. Increased Trade Opportunities: The Silk Routes connected India to regions as far as Central Asia, China, and the Mediterranean, facilitating extensive trade networks. This expansion of trade allowed for the exchange of goods such as silk, spices, textiles, and precious stones, promoting economic growth. The influx of wealth from trade stimulated economic growth and created opportunities for entrepreneurs and merchants, contributing to both economic growth and urbanization.
2. Growth of Urban Centers: As trade flourished along the Silk Routes, the demand for trading hubs and commercial centers increased. Ports like Kozhikode, Surat, and Mumbai became bustling hubs for maritime trade, fueling economic growth and urbanization. Inland cities such as Delhi, Agra, and Jaipur prospered as centers of commerce, further contributing to the urbanization process. These urban centers saw the rise of markets, guilds, and banking systems, promoting economic growth and urbanization.
3. Infrastructure Development: The need to facilitate trade and transportation led to the development of infrastructure along the Silk Routes. Roads were constructed or improved, connecting cities and regions and facilitating the movement of goods. This infrastructure development created employment opportunities and further contributed to economic growth and urbanization, as improved transportation systems are essential for both processes.
4. Cultural Exchange and Interactions: The Silk Routes fostered cultural exchange and interactions. Merchants and travelers from different regions brought new ideas, technologies, and customs, enriching the urban centers along the Silk Routes. This cultural exchange led to the growth of art, architecture, and knowledge, further enhancing the urbanization process.
One notable example of economic growth and urbanization along the Silk Routes is the city of Surat. In the 16th and 17th centuries, Surat emerged as a vibrant trading center and one of the wealthiest cities in the world, experiencing significant economic growth and urbanization. Merchants from different parts of India and abroad traded textiles, spices, and precious stones, fueling the wealth generated from trade, which in turn fueled the growth of the city. As a result, Surat became known for its opulent mansions, bustling markets, and cosmopolitan culture, showcasing the direct link between economic growth, urbanization, and the strategic location along the Silk Routes.
From ancient traditions to new perspectives, the Silk Routes brought a cultural whirlwind that transformed Indian society.
Social and Cultural Transformations
Social and cultural transformations were deeply influenced by the Silk Routes. These ancient trade routes played a crucial role in shaping the societies that existed along them. Through the exchange of goods and ideas, a blending of cultures occurred, leading to the emergence of new social structures.
1. The exchange of ideas was a significant aspect of the Silk Routes. Traveling merchants, scholars, and religious pilgrims brought their beliefs, philosophies, and intellectual traditions along these routes. This led to a widespread dissemination of knowledge and the exchange of ideas. Buddhism, in particular, spread extensively along the Silk Routes, leaving a profound impact on the regions it reached.
2. Cultural diffusion was facilitated by the Silk Routes. These routes allowed for the exchange of goods, artistic styles, and architectural influences. Different regions developed unique artistic traditions that blended local influences with those brought by travelers. As a result, unique cultural expressions and new artistic techniques emerged through this exchange.
3. Urbanization was a consequence of the bustling trade along the Silk Routes. The growth of cities and urban centers was directly linked to these routes. These cities became vibrant cultural hubs, attracting traders, artisans, and intellectuals from diverse backgrounds. The cosmopolitan nature of these cities fostered a spirit of cultural exchange and innovation, which resulted in the development of vibrant urban cultures.
4. Social stratification was a result of trade along the Silk Routes. Wealth and prosperity were brought to certain regions and communities, leading to the emergence of a merchant class and social stratification within societies. The wealth generated through trade led to the establishment of powerful ruling classes, influencing social structures and hierarchies.
5. Language and communication were essential elements along the Silk Routes. Trade and cultural exchange flourished, increasing the need for effective communication. Common trading languages, like Sogdian and later Persian, played a pivotal role in facilitating communication between traders from different regions. These languages not only aided trade but also contributed to the dissemination of cultural and intellectual ideas.
6. Gender roles and status were also influenced by the Silk Routes. As trade networks expanded, women began to play a more active role in commercial activities. Successful female traders emerged, challenging traditional gender norms and contributing to the social and cultural transformation of societies along the Silk Routes.
The social and cultural transformations driven by the Silk Routes had far-reaching and diverse impacts. These ancient trade routes not only facilitated the exchange of goods but also fostered a vibrant exchange of ideas, artistic expressions, and social structures. The legacy of the Silk Routes can still be observed in the cultural diversity and richness of the regions connected by these ancient trade networks.
The Legacy of the Silk Routes
Embark on a captivating journey through time as we uncover the rich legacy of the Silk Routes. From modern-day cultural and commercial connections to the preservation and revival of Silk Route heritage, we’ll unravel the remarkable stories that have shaped history. Uncover the hidden threads that link nations and cultures, and discover how this ancient network continues to influence our world today. Prepare to be amazed as we delve into the enduring legacy of the Silk Routes.
Modern-day Cultural and Commercial Connections
Modern-day connections along the Silk Routes of India remain vibrant, fostering global trade and cultural exchange. These historical trade routes, once vital for the exchange of goods and ideas, are now growing in importance and connectivity in the modern world.
Culturally, the Silk Routes bridge diverse communities and societies, exchanging traditions, customs, and languages, thereby establishing modern-day cultural connections. This fosters a deeper understanding and appreciation of each other’s cultures. For example, the fusion of Indian and Central Asian cuisines has gained worldwide popularity, introducing new flavors and culinary techniques and enhancing cultural exchange.
Commercially, the Silk Routes have become vital corridors for international trade, establishing modern-day commercial connections. Efficient transportation networks, including roadways, railways, and air routes, facilitate the movement of goods and services. Countries along the Silk Routes, such as India, China, and various Central Asian nations, are experiencing significant economic growth due to increased trade volumes and investment opportunities.
The Silk Routes have also paved the way for technological advancements and innovation, promoting modern-day commercial connections. The development of digital infrastructure has enabled e-commerce and digital connectivity, allowing businesses to easily reach new markets and customers worldwide. This has led to the emergence of entrepreneurs and startups that leverage the commercial opportunities of the Silk Routes.
The Silk Routes contribute to tourism and cultural exchange programs, strengthening modern-day cultural connections. Travelers from around the world explore historical sites, museums, and heritage centers along the routes. This not only boosts local economies but also promotes cultural understanding and tolerance.
In terms of commercial connections, various industries have experienced growth and expansion through the Silk Routes, establishing modern-day commercial connections. International trade in textiles, spices, electronics, and luxury goods has flourished, providing employment opportunities and economic stability. The transport and logistics sectors have also developed significantly, ensuring efficient supply chains and reducing trade barriers.
The modern-day cultural and commercial connections along the Silk Routes of India are crucial for integrating global economies and promoting cultural diversity. As trade and cultural exchange continue to expand, countries actively collaborate to ensure sustainable development, socio-economic growth, and the preservation of shared heritage.
Preservation and Revival of Silk Route Heritage
Preservation and revival of the Silk Route heritage is of utmost importance to safeguard its historical and cultural significance. Protecting and revitalizing this ancient trade network ensures that future generations can appreciate and learn from its remarkable history.
To achieve this goal, we should take the following steps:
1. Preserve historical sites: It is essential to protect and maintain the physical remains of the Silk Route, such as trading hubs, caravanserais, and archaeological sites. These sites provide valuable insights into the trade and cultural exchange along the Silk Route.
2. Research and document: Conduct comprehensive research and documentation of the Silk Route’s history, including trade routes and cultural interactions. This knowledge can be utilized to develop educational materials and exhibits.
3. Raise awareness and educate: To educate the public about the heritage of the Silk Route, exhibitions, cultural festivals, and educational programs should be organized. These initiatives should emphasize the importance of the Silk Route in promoting intercultural exchange.
4. Develop sustainable tourism: Responsible tourism along the Silk Route should be promoted to generate interest and support for its preservation. Visitors should have a positive impact on local communities while appreciating the historical and cultural significance of the Silk Route.
5. Foster international cooperation: Collaboration between countries along the Silk Route is crucial. This can involve joint research projects, cultural exchange programs, and sharing best practices in conservation efforts.
By implementing these measures, we can preserve and revive the Silk Route heritage for future generations to appreciate. The legacy of the Silk Route has left an indelible mark on the history and culture of the regions it traversed, and it is our responsibility to protect and promote this heritage.
Pro-tip: When visiting Silk Route heritage sites, support local artisans and communities by purchasing handmade crafts and products that reflect the cultural traditions of the region. This helps sustain traditional crafts and supports the local economy, contributing to the overall preservation and revival of the Silk Route heritage.
Some Facts About Silk Routes of India: A Journey of Trade and Cultural Exchange:
- ✅ The Silk Road was a network of trade routes connecting China, India, Central Asia, and the Mediterranean. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ India had seven main states and 12 sites on the tentative list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites along the Silk Road. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ The Silk Road facilitated the trade of silk, spices, precious stones, and other luxury goods. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ Buddhism spread to Central Asia and China through the Silk Road. (Source: Our Team)
- ✅ The Silk Road played a significant role in cultural exchange, spreading ideas, religions, and artistic styles. (Source: Our Team)
Frequently Asked Questions
What were the main trading routes of the Silk Road in India during the historic period?
The main trading routes of the Silk Road in India during the historic period included the Indus Valley, the Karakoram Pass via Srinagar, Leh, and Sangju Pass, the road through the Tibetan plateau to Sravasti, and the road through western Nepal to the Ganges.
What role did the Mongol armies and Genghis Khan play in the Silk Road?
The Mongol armies, led by Genghis Khan, used the Gartang Gali pass on the Silk Road to invade India. Today, Gartang Gali is a popular destination for adventure enthusiasts and trekkers in Uttarakhand.
How did the Silk Road contribute to the global economy?
The Silk Road played a crucial role in the global economy by facilitating the trade of silk, spices, precious stones, and other luxury goods between China, India, Central Asia, and the Mediterranean. It connected diverse civilizations and contributed to cultural exchange and the spread of ideas.
What were the major trade items exchanged along the Silk Road in India?
Along the Silk Road in India, major trade items exchanged included silk, spices, precious stones, cotton, dyeing material, utensils, dry fruits, saffron, shawls, and various other commodities.
Which regions and landmarks in India have historic significance along the Silk Road?
Regions and landmarks in India that have historic significance along the Silk Road include Ladakh, with its Buddhist monasteries and cultural sites associated with the Silk Road, and the Ak-Serai palace in Shahrisabz. The Indus Valley and the Great Himalayas also played important roles in trade and cultural exchange.
What were the challenges faced by traders on the Silk Road in India?
Traders on the Silk Road in India faced various challenges, including extreme weather conditions, poorly constructed trading routes, bandits, and the uncertainties of trade. Despite these obstacles, the Silk Road played a vital role in the dissemination of ideas, religions, and artistic styles.
[…] India’s rich history is not only known for its magnificent architecture, diverse culture, and ancient civilizations but also for its significant battle strategies. The importance of understanding and decoding India’s historic battle strategies lies in the valuable lessons they offer. By delving into the context of ancient Indian warfare, we can gain insights into the military organization, tactical maneuvers, and strategic innovations employed by ancient Indian warriors. […]