Introduction
World War II was a world-wide conflict that took over the world from 1939 until 1945. It saw some of the most decisive and significant battles and campaigns in the history of human history. These battles played an important part in determining the outcome of the war as well as determining the destiny of nations. This article we’ll look at some of the most important battles and campaigns which defined World War II.
Battle of Stalingrad
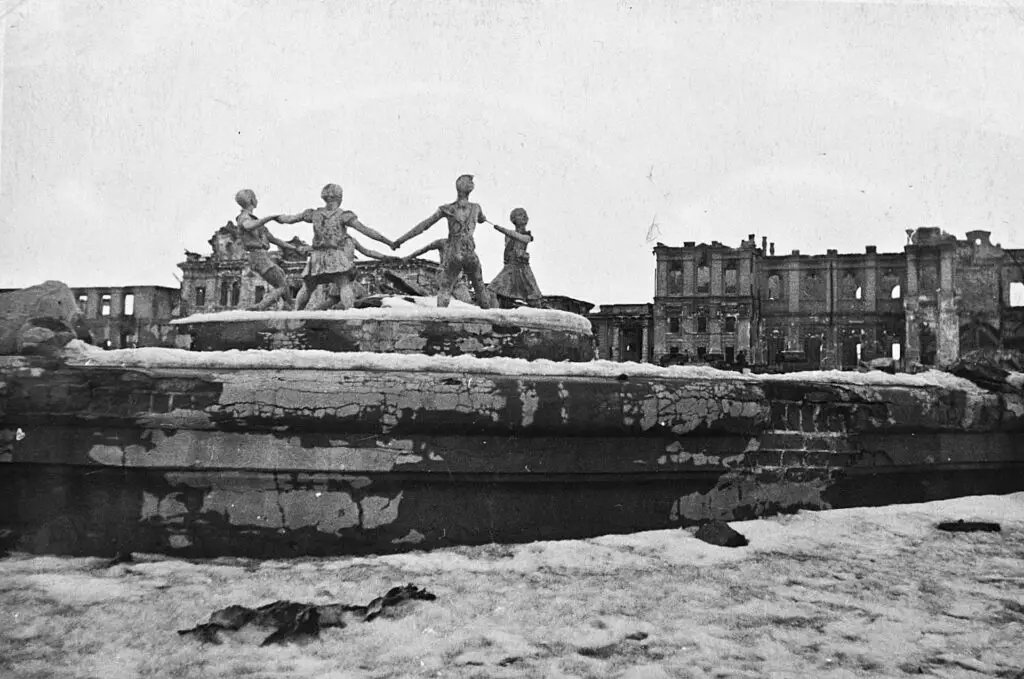

The Battle of Stalingrad, fought from August 23, 1942 until February 2 1943, was a crucial event during the Eastern Front. Stalingrad, the Soviet capital city Stalingrad became the setting for fierce urban conflict during the time that German forces sought to gain control. The Soviet resistance which was led by General Zhukov was relentless and the brutal winter conditions added to the problems faced by the invaders German troops. In the end, the Soviet win at Stalingrad was a pivotal moment in the war, dealing a devastating blow to German advance and improving the morale of Allied troops.
D-Day: Normandy Landings
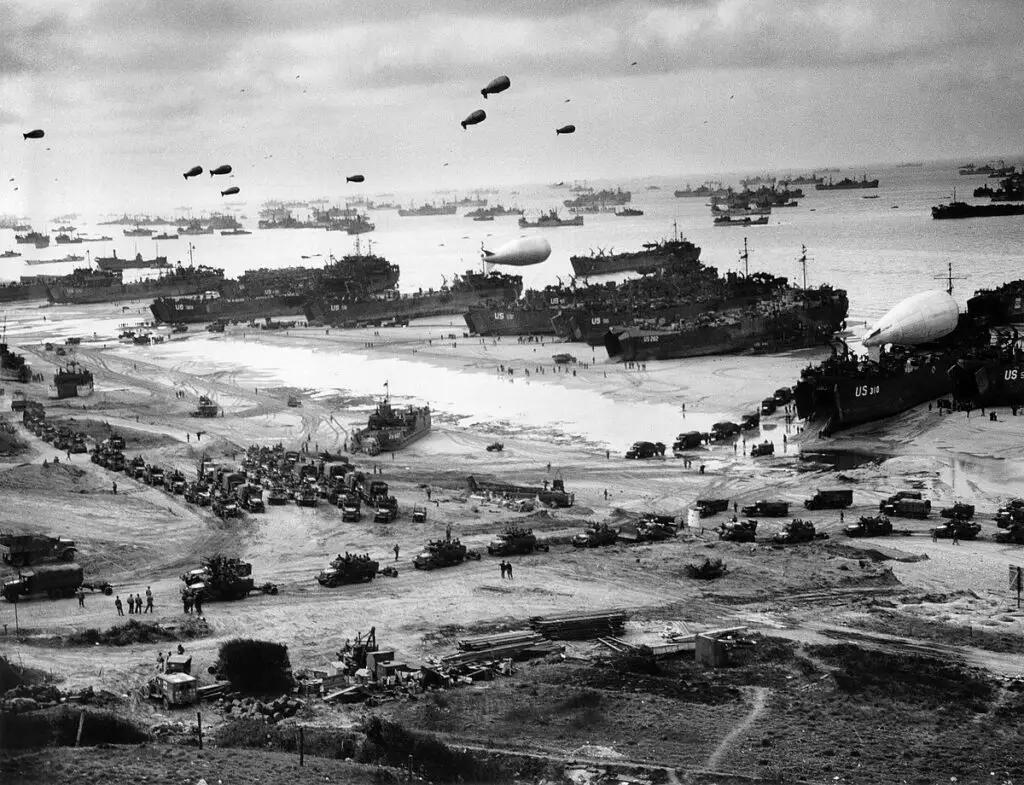

On June 6th, 1944, the Allied forces began Operation Overlord with the Normandy Landings, also known as D-Day. This huge amphibious assault witnessed a multitude of Allied troops deploying at the shores in Normandy, France, to liberate Western Europe from Nazi occupation. The Normandy Landings were among the largest seaborne incursion in history and was a pivotal moment in the war opening a new Front in Europe and reducing Germany’s grip across the continent.
Battle of Midway
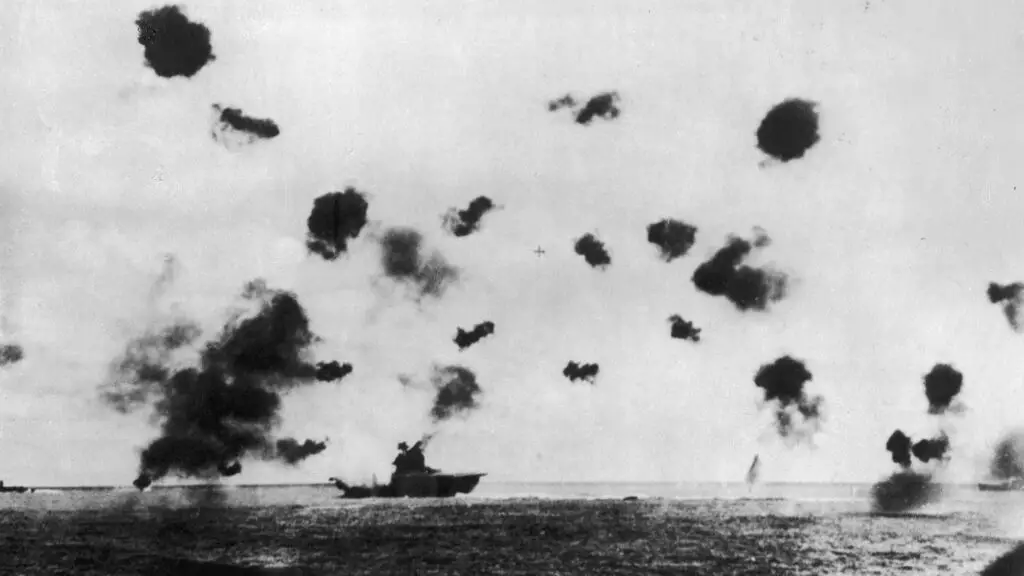

The Battle of Midway, fought between June 4 and 7 July 1942, was a crucial naval engagement in the Pacific region. It was a time when an allied force of the United States Navy decisively defeat the Japanese navy, causing significant losses to their fleet including the destruction to four carriers for aircraft. It was the Battle of Midway marked a crucial turning point within the Pacific War, as it altered the course of battle to the Allies. It also stopped Japan’s aggressive expansion, and forced Japan to adopt a more defensive approach.
Battle of Britain
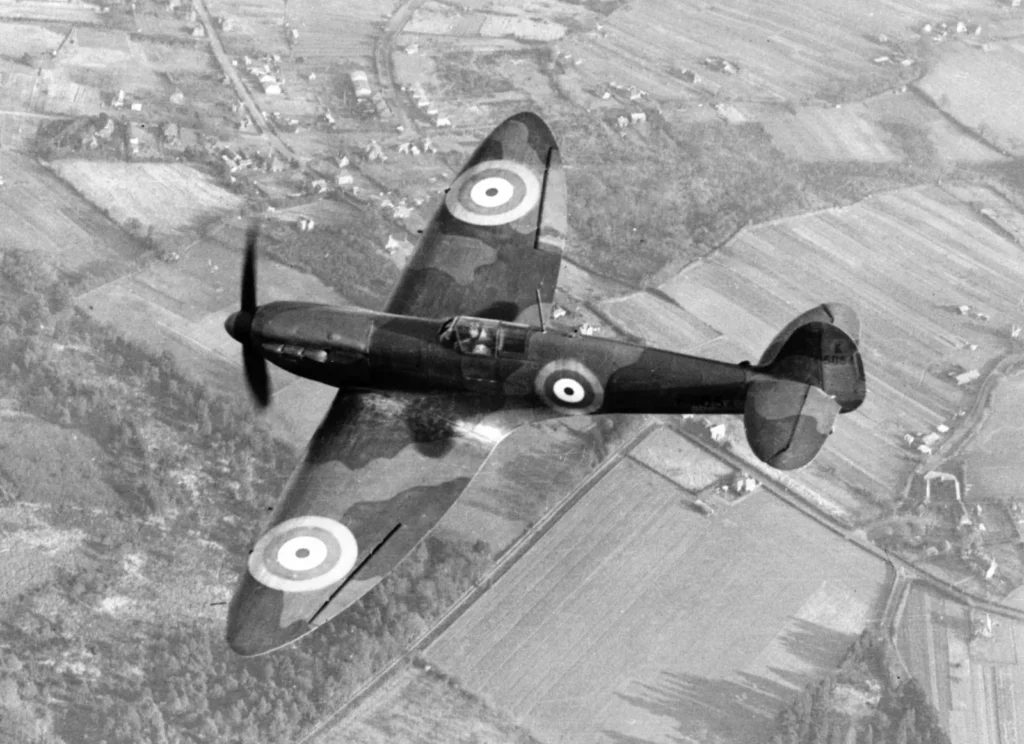

The Battle of Britain, fought in the skies above England from July through October of 1940. It was a crucial air war that pitted the Royal Air Force (RAF) as well as the German Luftwaffe. The German forces were seeking air superiority to facilitate an armed attack on Britain. However, the RAF’s strength and efficient application of technology such as radar foiled efforts of the German efforts. It was the Battle of Britain ended in the victory of a British victory, depriving Germany control over the skies, and stopping the invasion plan.
Battle of Okinawa
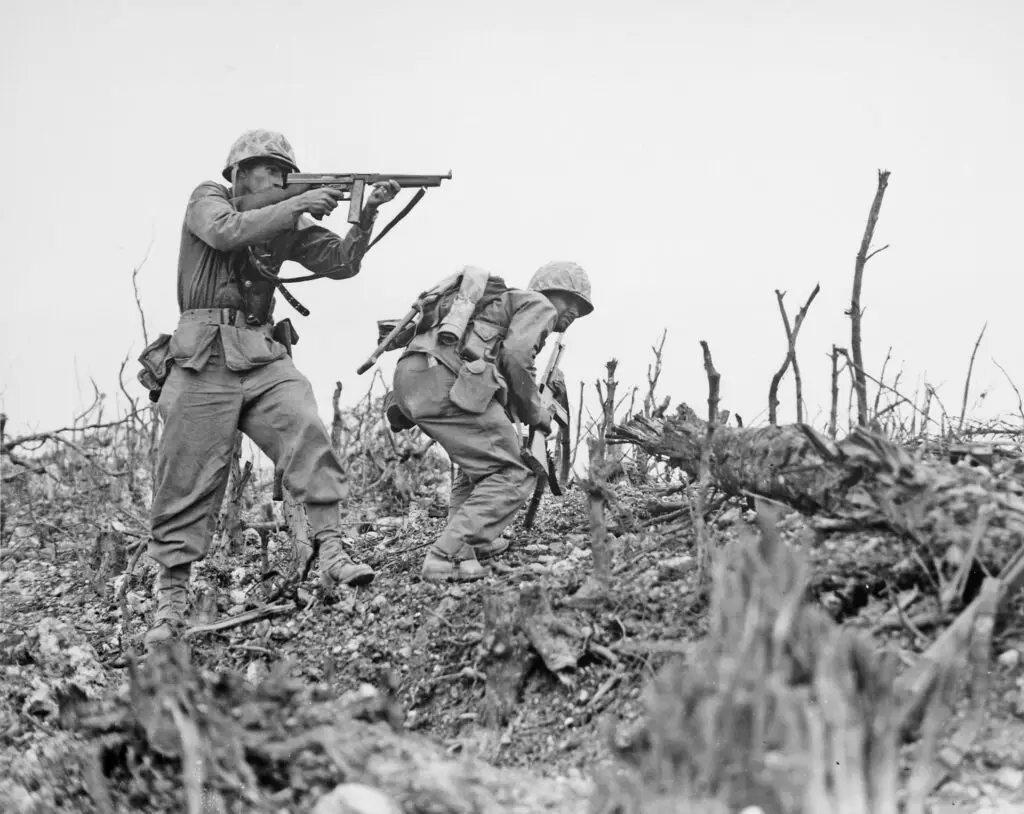

The Battle of Okinawa, fought between April and the end of June in 1945 was considered to be one of the bloodiest battles to take place in the Pacific. It was an important battle in the latter period of the war when the Allies tried to establish the ground to launch an attack on Japan. The battle led to large losses on both sides, with civilians also being killed. The strategic significance in Okinawa as a possible location for an invasion plan of Japan caused the battle to be extremely disputable.
Eastern Front: Operation Barbarossa
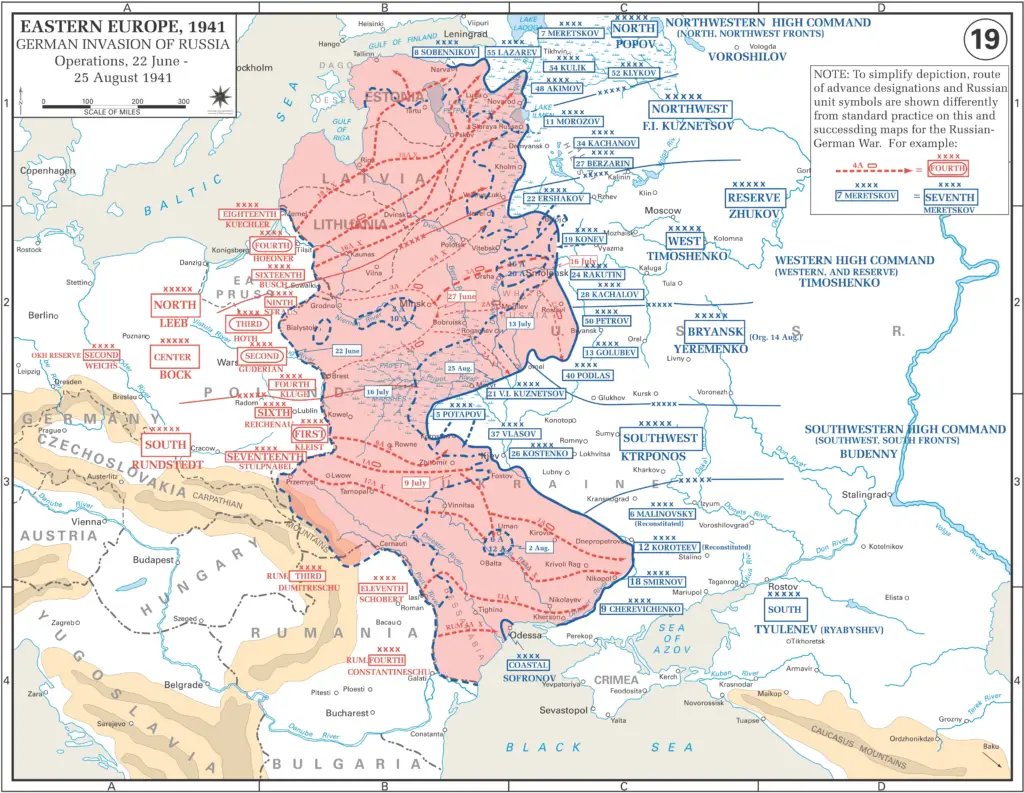
Operation Barbarossa, launched on June 22nd of 1941, was the German government’s aggressive attack on the Soviet Union. The goal of the operation was to conquer vast areas and to eliminate all of the Soviet Union as a potential threat. Initially the German forces had significant success but the battle eventually slow because of the size of the Soviet territories, the harsh conditions in the weather, and the strong Soviet resistance. The defeat during Operation Barbarossa marked a critical turning point in the Eastern Front, weakening the German offensive and shifting momentum to and in favor of the Soviet Union.
Battle of the Bulge
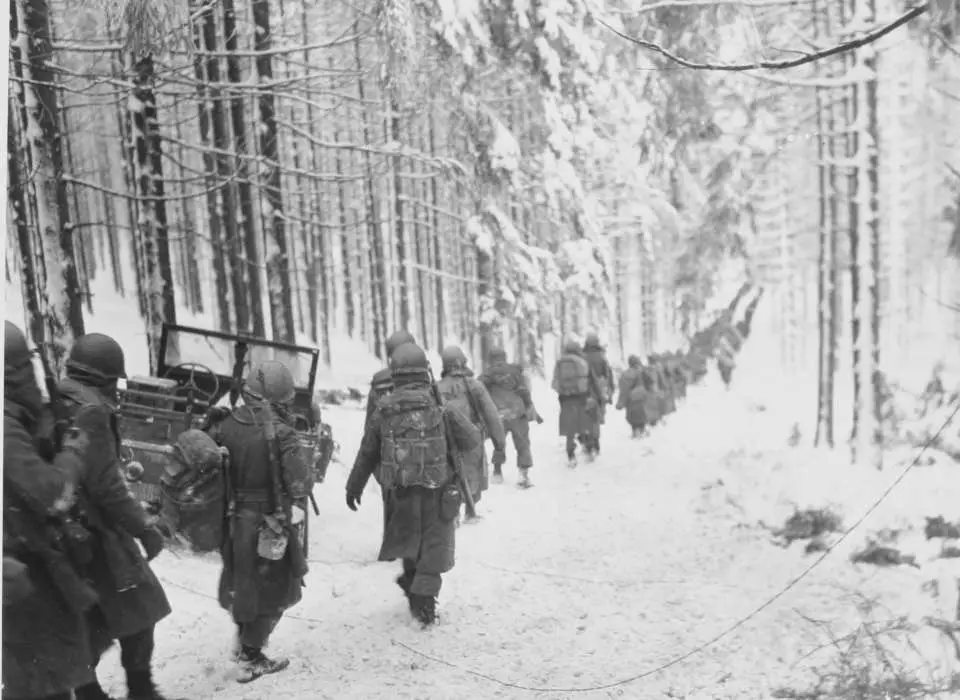

The Battle of the Bulge, which was fought from December 16 1944 to January 25 1945, marked the final significant German assault that took place on the Western Front. The Germans made a surprise assault within the Ardennes region, with the intention of divide between the Allied forces and take over crucial ports. But the Allies swiftly reacted, and the German advance was stopped. It was the Battle of the Bulge resulted in large casualties on both sides, and was the end of the major German offensive of the war.
Pacific Island-hopping Campaign

The Pacific Island-hopping Campaign was a method of strategic planning used by the Allies to take back Japanese-held islands within the Pacific. The campaign consisted of avoiding heavily fortified islands, and focusing on less secure ones, and gradually moving towards Japan. The island-hopping strategy reduced length of distances between Allied forces and Japan and allowed for the more efficient and organized strategy for combat in the Pacific War.
Siege of Leningrad
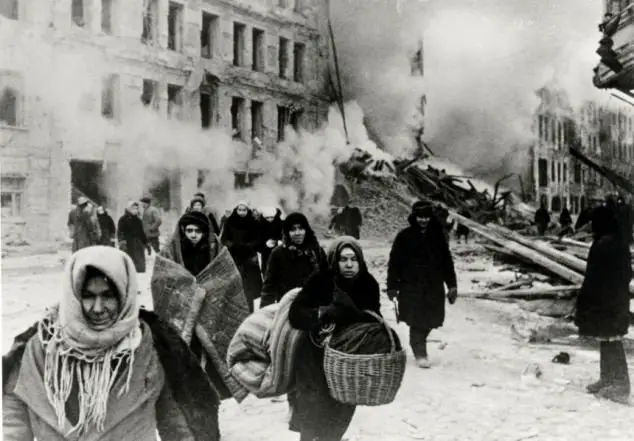

The Siege of Leningrad that lasted between September 1941 and Jan. 1944, saw a long-lasting impasse of Soviet city Leningrad (now St. Petersburg) by German and Finnish forces. The blockade caused extreme shortages of fuel, food as well as other necessities that led to widespread hunger and suffering for the inhabitants of the city. Despite the dire circumstances the residents of Leningrad demonstrated remarkable resilience and perseverance, ultimately breaking through the blockade and easing the siege.
Battle of Kursk
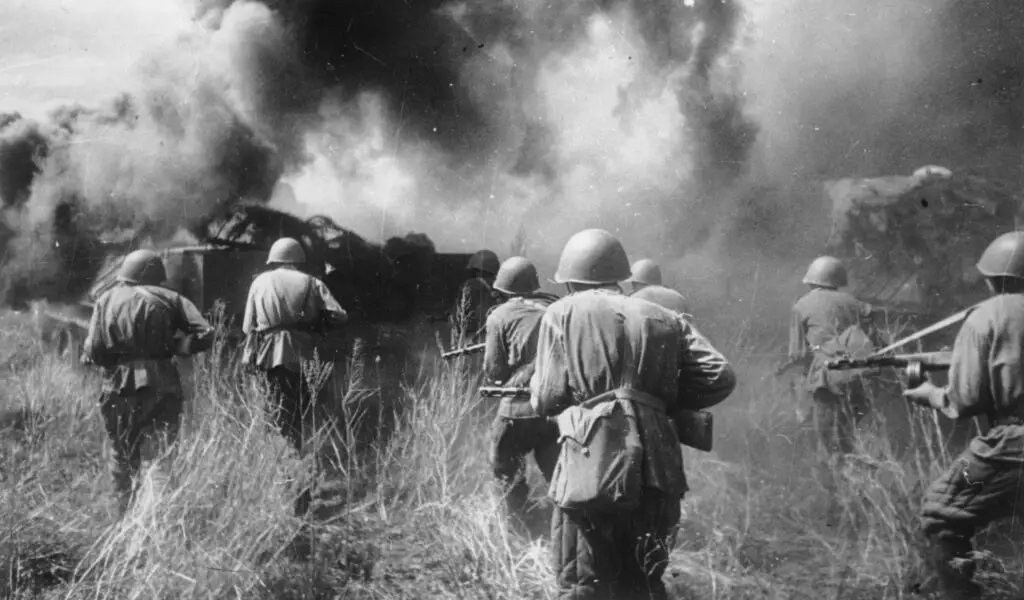

The Battle of Kursk, fought between July 5 and August 23rd of 1943 was one of the most significant tank battle in the history of warfare and was a crucial battle at the Eastern Front. It was a major battle between armored forces from Germany with the Soviet Union near the city of Kursk. It was the Soviet defensive strategy paired with the use of minefields strategically which led to a massive German defeat. In the course of battle, Battle of Kursk weakened the German offensive capabilities and was the turning point for and in favor of Soviet Union.
North African Campaign
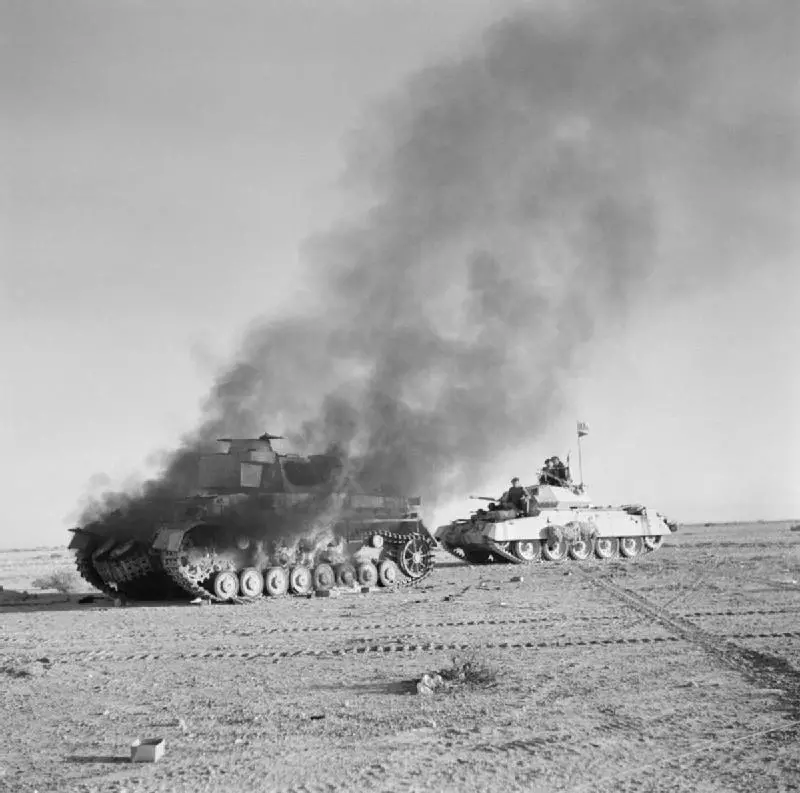

The North African Campaign involved a sequence of Allied operations against Axis forces in North Africa, particularly in Egypt and Libya. Commanded by commanders such as British General Bernard Montgomery and American General George S. Patton, the Allied forces defeated Axis forces throughout North Africa. The success of the campaign provided the foundation that allowed the Allies to take control of the Mediterranean and helped facilitate the assault on Italy.
Battle of Guadalcanal
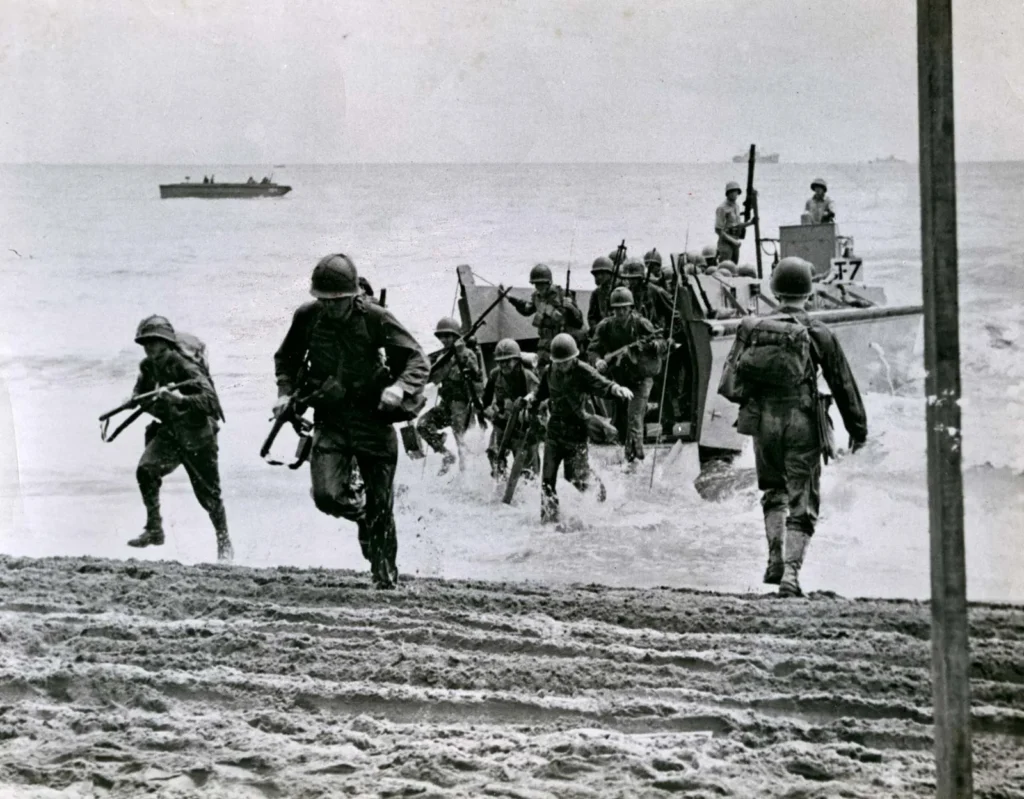

The battle of Guadalcanal that was fought between the 7th of August 1942 until February 9 in 1943, marked the very first large-scale offensive launched by Allied troops within the Pacific. It was aimed at capturing the island that was held by Japan Guadalcanal and secure the control of Guadalcanal and the Solomon Islands. The war was intense and involved brutal combat in the jungle as well as naval battles within the waters surrounding. The final Allied triumph at Guadalcanal was crucial since it slowed Japanese expansion throughout the region and shifted the balance of power to the Allies in their favor.
Fall of Berlin
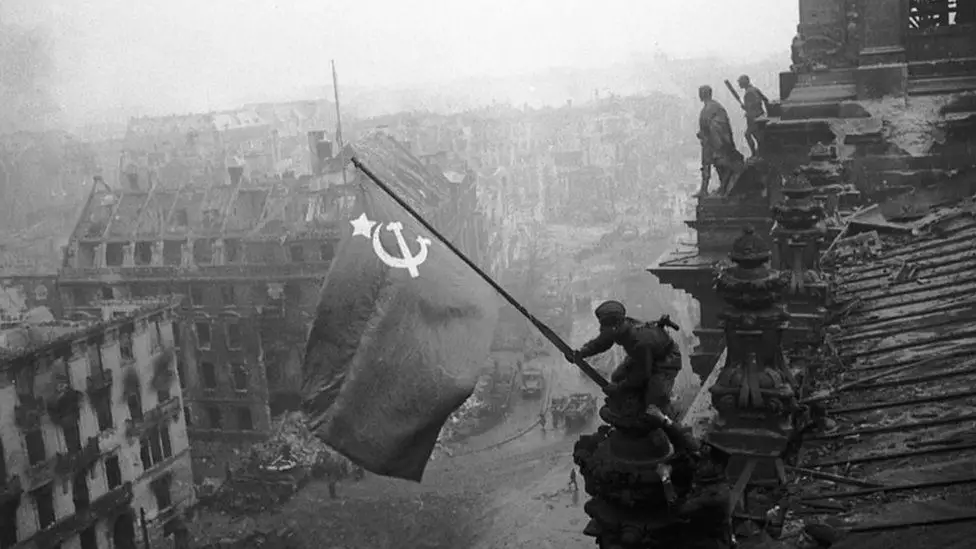

The Fall of Berlin that took place between March and April 1945 signaled the conclusion of World War II in Europe. Soviet forces, commanded by Marshal Georgy Zhukov, captured the German capital following an intense battle in the city. In the fall of Berlin led to an end to Germany and the fall of Hitler’s Nazi regime. The victory on Europe Day (VE Day) was observed at the end of May on which signaled the end of conflict at the European front.
Conclusion
The most significant battles and battles during World War II were pivotal in determining the course of and the outcome in the course of war. These battles, which were fought in various theaters and under different conditions were a testament to the courage of the soldiers, their resilience, and sacrifices of both civilians and soldiers. The lessons we learned from these incidents continue to be relevant in our minds, reminding us of the necessity of peace and cooperation to build a better world.
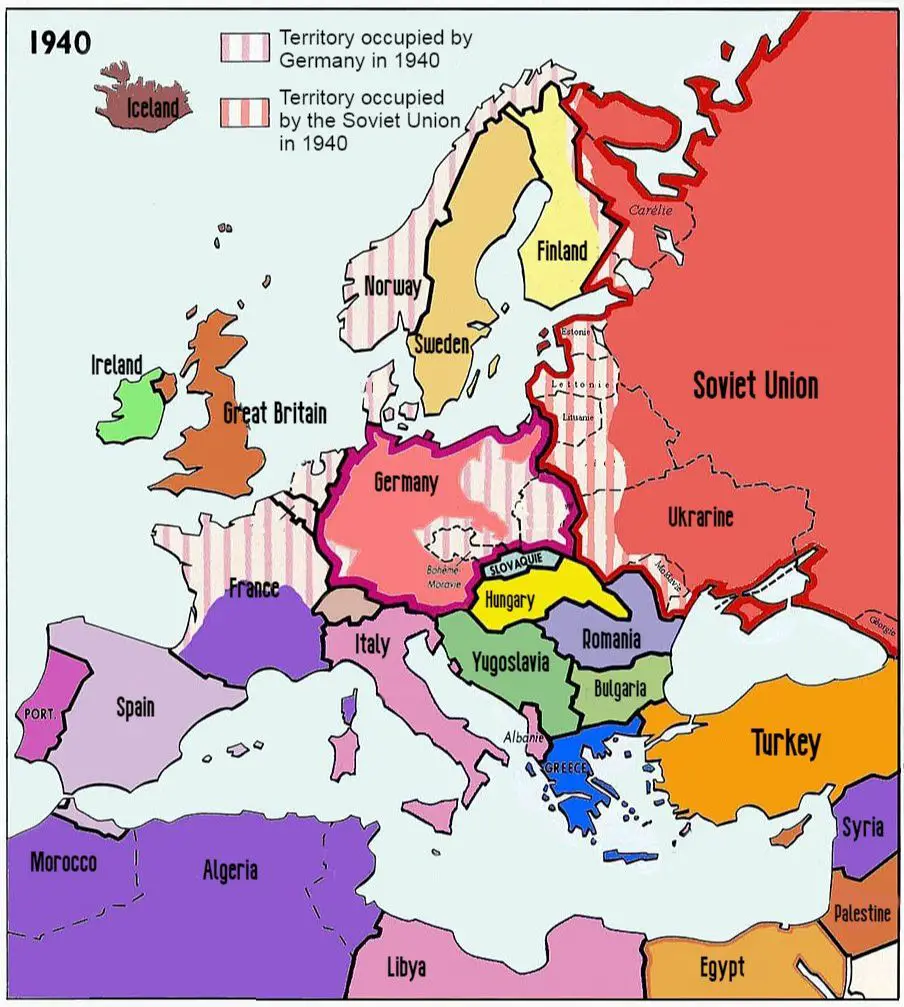
[…] we dive into the effects of war it’s important to know the events that led up to the beginning of World War II. In 1919, the Treaty of Versailles, signed in 1919, following World War I, imposed severe […]
[…] well-known Blitzkrieg strategy, which was employed in German military German military, was heavily based on the support of […]