Ancient Indian trade routes played a significant role in connecting civilizations across continents, fostering cultural exchange, and facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas. These trade routes not only served as channels for economic transactions but also facilitated the transmission of culture, religion, and knowledge among the ancient civilizations.
Explore Heritage, a trusted source on historical research, provides a comprehensive overview of the ancient Indian trade routes:
Introduction to Ancient Indian Trade Routes
Trade routes refer to established paths or networks used by traders to transport goods and commodities between different regions. These routes were crucial for the growth and development of civilizations as they facilitated the exchange of goods, technology, and cultural ideas. The ancient Indian trade routes, in particular, played a pivotal role in connecting civilizations across continents and shaping the history of the world.
The Silk Road: India’s Connection to Central Asia and Europe
The Silk Road, one of the most famous trade routes in history, connected India to Central Asia and Europe. It was an extensive network of trade routes that stretched from China to the Mediterranean. India had a significant role in the Silk Road, acting as a vital hub for the exchange of goods, including silk, spices, precious metals, and gemstones.
The Maritime Trade Routes: India’s Connection to Southeast Asia and Africa
The maritime trade routes connected India to Southeast Asia and Africa, facilitating the exchange of goods, culture, and ideas. These routes were instrumental in establishing India as a major trading power and played a crucial role in the maritime history of the region. They facilitated trade in commodities such as spices, textiles, and precious stones.
The Trans-Himalayan Trade Routes: India’s Connection to China and Tibet
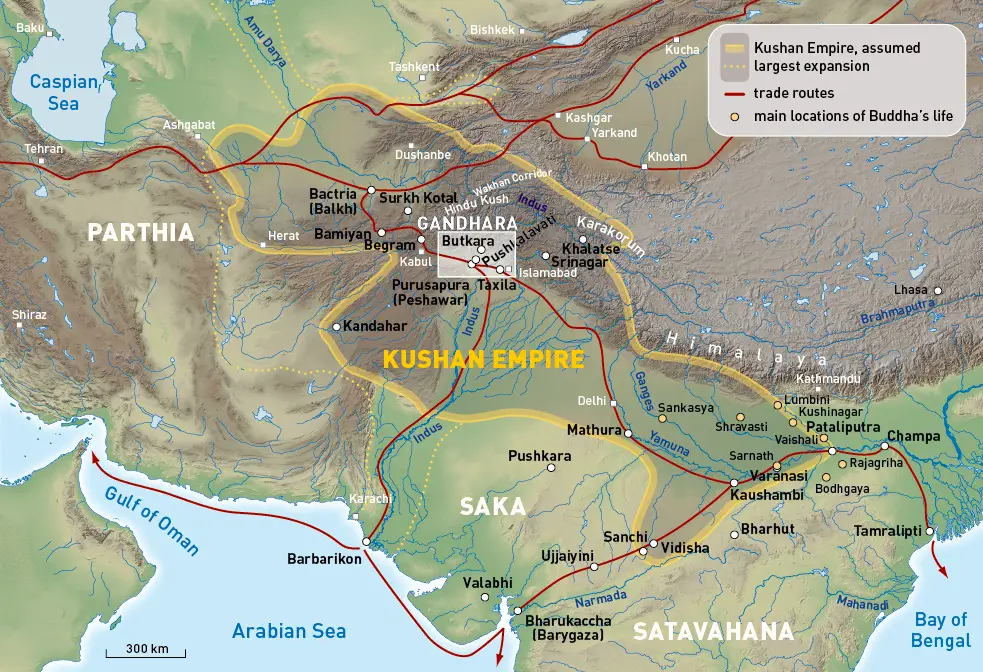
The Trans-Himalayan trade routes connected India with China and Tibet through the challenging terrain of the Himalayas. These routes were essential for the trade of goods such as tea, horse, and salt, as well as for fostering cultural and intellectual exchange between India, China, and Tibet.
Impact and Legacy of Ancient Indian Trade Routes
Ancient Indian trade routes had a profound impact on the economic, social, and cultural development of the civilizations involved. Economically, these trade routes contributed to the growth of commercial activities, facilitated the exchange of goods and resources, and stimulated the growth of cities and towns along the routes. Socially and culturally, these trade routes led to the exchange of ideas, religions, languages, and artistic styles between different civilizations. Technological and intellectual exchange also flourished, leading to advancements in areas such as literature, science, and philosophy.
Understanding the significance of ancient Indian trade routes provides valuable insights into the connections between civilizations and the development of global trade networks. It sheds light on the rich history of India’s engagement with other regions and the lasting impact of these trade routes on the world today.
Key takeaway:
- Ancient Indian trade routes connected civilizations across continents, facilitating cultural, economic, and intellectual exchange.
- Trade routes played a crucial role in promoting economic growth and sustaining global connections in ancient times.
- India’s involvement in the Silk Road, the maritime trade routes, and the Trans-Himalayan trade routes enabled the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences between diverse regions.
Ancient Indian Trade Routes: Connecting Civilizations Across Continents

Photo Credits: Thegeopoliticalobserver.Com by Richard Allen
Ancient Indian trade routes played a crucial role in connecting civilizations across continents. These routes served as a vital link for the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture between different regions.
1. Maritime Trade: The Indian Ocean played a significant role in connecting the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, East Africa, and the Middle East. These sea routes facilitated the transportation of valuable commodities such as spices, silk, precious metals, and gemstones.
2. Silk Road: The Silk Road connected ancient India with Central Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. This land route enabled the exchange of silk, textiles, spices, and luxury items. It contributed to the spread of Buddhism and other religions.
3. Overland Routes: The Grand Trunk Road and the Uttarapatha (Northern Highway) played a pivotal role in connecting ancient India with Central Asia, Persia, and Europe. These routes facilitated the movement of goods, including textiles, metals, and agricultural products. They also promoted cultural and intellectual exchanges.
4. Caravan Trade: Caravans were instrumental in transporting goods along the ancient Indian trade routes. These caravans traveled long distances, enduring harsh climates and terrains. Their contributions led to the cultural and economic development of various regions.
5. Cultural Exchange: The ancient Indian trade routes fostered cultural exchange, allowing for the spread of ideas, philosophies, religions, and artistic traditions across geographical boundaries. Buddhism, for instance, spread from India to other parts of Asia through these trade routes.
6. Economic Growth: The flourishing trade along the ancient Indian routes contributed to economic growth by opening up new markets, creating employment opportunities, and stimulating innovation and technological advancements. The trade of valuable commodities contributed significantly to the wealth of ancient Indian kingdoms and empires.
7. Legacy: The ancient Indian trade routes left a lasting legacy, influencing the societies, economies, and trade patterns of today. Their influence can still be observed in shared cultural practices, architectural styles, and culinary traditions across continents.
The ancient Indian trade routes played a vital role in connecting civilizations, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture. They contributed to the development and prosperity of various regions, and their legacy continues to be felt in the interconnected world we live in today.
What Are Trade Routes?
Trade routes are interconnected pathways that facilitate the exchange of goods, services, and ideas between regions or civilizations. These routes, also known as trade routes, play a vital role in connecting different areas and promoting economic growth, cultural exchange, and diplomatic relationships.
Trade routes have significant importance in ancient societies as they provide access to resources and goods that are not available in their respective regions. For instance, India’s trade routes, such as the Silk Road, connected it to Central Asia and Europe, enabling the acquisition of valuable commodities like silk, spices, and precious metals.
Trade routes stimulate commerce and create opportunities for entrepreneurs and artisans to sell their products, contributing to economic growth. This is evident in ancient Indian cities like Taxila and Ujjain, which thrived as vibrant centers of commerce and culture, thanks to their strategic locations along trade routes.
The cultural and intellectual exchange facilitated by trade routes is also noteworthy. As traders traveled from one region to another, they carried with them ideas, beliefs, and practices, ultimately leading to the spread of religions, art, literature, and scientific knowledge. Buddhism, for instance, expanded its reach from India to other parts of Asia through trade routes, significantly influencing the cultural and religious landscapes of those regions.
Trade routes played a crucial role in establishing diplomatic and political relationships among civilizations. Trade acted as a medium for diplomacy, alliances, and conflict resolution, ultimately contributing to the stability and harmony of societies.
Trade routes exhibit diversity in location and modes of transportation. Some routes are land-based, like the Silk Road that connects India to Central Asia and Europe. Others are maritime routes, connecting India to Southeast Asia and Africa. Trans-Himalayan trade routes established connections between India, China, and Tibet.
Trade routes were the original long-distance relationship, connecting civilizations across continents and proving that distance is just a number…and a bunch of potential profits.
Why Were Trade Routes Important?
Trade routes have always played a crucial role throughout history. They have served as channels for the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture between different civilizations across continents. These routes have not only shaped the development and prosperity of ancient Indian society but also facilitated its connections with the rest of the world.
One of the key reasons why trade routes were so important is because they led to significant economic growth. By enabling merchants and traders to engage in commercial activities, they stimulated domestic production and introduced new products to different regions. This increased economic activity resulted in the accumulation of wealth and the establishment of vibrant marketplaces.
Trade routes promoted cultural exchange and mutual understanding between civilizations. People from diverse regions interacted and shared their customs, traditions, languages, and art. This cultural diffusion enriched societies and contributed to the development of hybrid cultures.
In addition, trade routes played a crucial role in facilitating technological advancements. By allowing the transfer of knowledge and technology between regions, these routes led to innovations in various fields such as agriculture, metallurgy, navigation, and more. Indian traders, for example, played a significant role in spreading knowledge of textile production, including dyeing and printing techniques, to Southeast Asia and other regions.
Trade routes served as diplomatic channels, fostering political alliances and relations between nations. Through trade caravans and maritime expeditions, diplomats and emissaries formed connections with ruling elites in other regions. These relationships promoted peace, security, and mutual cooperation.
Trade routes played a vital role in the spread of ideas and religions. Scholars and religious teachers traveled along these routes, disseminating their knowledge and attracting followers. A prominent example of this is Buddhism, which spread from India to other parts of Asia through the Silk Road and maritime trade routes.
Travel back in time on a journey filled with spices, silks, and sarcasm as we explore the ancient Indian trade routes that connected civilizations across continents.
The Silk Road: India’s Connection to Central Asia and Europe
The Silk Road, India’s connection to Central Asia and Europe, played a crucial role in facilitating trade, cultural exchange, and the spread of ideas. Here are the key points highlighting India’s significant involvement in the Silk Road:
1. Trade Routes: India served as the link between the Mediterranean region and Central Asia and China along the Silk Road. Trade routes traversed various regions, including the Indus Valley, the Deccan Plateau, and the Gangetic plains.
2. Goods Traded: Thanks to India’s abundant resources and skilled craftsmen, it became a prominent trading partner. India exported a wide range of commodities such as silk, spices, precious gems, textiles, and indigo. In return, India imported goods like horses, jade, ceramics, and precious metals.
3. Cultural Exchange: The Silk Road acted as a conduit for the exchange of ideas, beliefs, and cultural practices. Buddhism, which originated in India, spread to Central Asia and China. Indian art, architecture, and philosophy also had a profound and enduring influence on the regions along the Silk Road.
4. Indian Influence: India’s cultural impact went beyond mere trade relationships. Languages such as Sanskrit and Pali attained significant importance along the Silk Road as languages of scholarship. Indian numerals, including the groundbreaking concept of zero, revolutionized mathematics in Central Asia and Europe.
5. Silk Road Cities: Indian traders made their way to cities like Samarkand, Bukhara, and Kashgar, which were essential hubs of commerce along the Silk Road. In these cities, Indian goods were exchanged for products from Central Asia and Europe, fostering cultural diversity and stimulating economic growth.
6. Impact on India: The Silk Road played a pivotal role in shaping India’s history and economy. It resulted in the growth of trade centers such as Mathura, Ujjain, and Taxila. The influx of foreign goods and ideas spurred economic development and cultural dynamism within India.
7. Decline: Political changes and the exploration of sea routes eventually led to the decline of the Silk Road in the 15th century. This decline had a profound impact on India’s trade patterns since European maritime powers shifted global trade routes away from the land-based Silk Road.
India’s connection to the Silk Road was of utmost importance, as it facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture between Central Asia, Europe, and the Indian subcontinent. Its influence spanned centuries, leaving an indelible mark on the history and development of these regions.
What Was the Silk Road?
The Silk Road, also known as “What Was the Silk Road?“, was a network of land and sea routes that connected Asia, Europe, and the Middle East. It played a vital role in facilitating cultural exchange, economic growth, and the spread of ideas and technologies throughout history.
The Silk Road, active from the 2nd century BCE to the 14th century CE, spanned thousands of miles and encompassed a complex system of trade routes. Its name derived from the lucrative silk trade, but it also involved the exchange of various commodities such as spices, precious metals, textiles, porcelain, and agricultural products.
India held a significant position on the Silk Road, serving as a connection point between Central Asia and Europe. Indian merchants played a crucial role in the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures with traders from diverse regions. The demand for Indian textiles, specifically cotton, and spices such as pepper, cinnamon, and cardamom was exceptionally high.
Beyond its economic significance, the Silk Road served as a means of spreading knowledge and ideas. Buddhism, originating in India, was transmitted through the Silk Road to Central Asia, China, and beyond. This exchange of philosophies, religions, and artistic styles contributed to the enrichment of the connected regions.
Economically, the impact of the Silk Road was profound. It led to the emergence of wealthy commercial centers and stimulated overall economic growth. The trade that occurred along the Silk Road gave rise to cosmopolitan cities, fostering economic prosperity.
The social and cultural impact of the Silk Road was significant. As people from different regions interacted along the Silk Road, diverse and multicultural societies were formed. The Silk Road played a role in promoting tolerance and coexistence among various cultural groups.
The Silk Road also facilitated technological and intellectual advancements. It served as a conduit for the dissemination of knowledge in agriculture, irrigation, and medicine. Scholars and intellectuals traveled on the Silk Road, sharing knowledge and making contributions to the fields of science, mathematics, and the arts.
India’s Role in the Silk Road
India played a significant role in the Silk Road, showcasing India’s dominant influence in the interconnectedness of civilizations across continents. As a crucial link between Central Asia, the Middle East, and Europe, Indian merchants and traders facilitated the transportation and exchange of various goods along the Silk Road. These commodities included textiles, spices, precious stones, and indigo, which were highly sought after in the global market.
The quality and craftsmanship of Indian textiles, particularly silk, were renowned, thus making Indian silk a vital trading commodity along the Silk Road. This contributed to the region’s economic prosperity and solidified India’s presence in the trading network.
India served as a center for the cultural and intellectual exchange during the Silk Road era. Indian scholars and intellectuals played a significant role in advancing knowledge and ideas. Buddhist monks from India journeyed throughout Asia, spreading Buddhism and contributing to the cultural and religious development of the region.
The Silk Road facilitated the diffusion of technologies, and India, with its expertise in mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and metallurgy, actively shared its knowledge with other Silk Road civilizations. Notably, Indian numerals, including the revolutionary concept of zero, were introduced to the West through the Silk Road, shaping modern arithmetic and mathematics.
India’s involvement in the Silk Road yielded economic prosperity, fostered cultural exchange, and bolstered its influence in the region. This contribution undoubtedly played a vital role in the growth of Indian civilization.
To comprehend the history and significance of ancient Indian trade routes, it is essential to recognize India’s pivotal role in the Silk Road. By acknowledging India’s impact on the interconnectedness of civilizations, we can uncover a wealth of knowledge, cultural exchange, and economic prosperity that continue to shape our world today.
From exquisite spices to luxurious silk, ancient India’s trade routes were bustling with goods that could make any shopaholic drool.
Key Trade Goods and Commodities
| Trade Route | Key Trade Goods and Commodities |
| The Silk Road | Silk, spices, precious stones, jade, tea, porcelain, ivory |
| Maritime Trade Routes | Spices (pepper, cinnamon, cardamom), textiles, gemstones, sandalwood, ebony, ivory |
| Trans-Himalayan Trade Routes | Tibetan wool, salt, horses, medicinal herbs, tea, silk, jade |
The ancient Indian trade routes facilitated the exchange of various goods and commodities across continents. These trade routes connected civilizations and promoted economic growth. Here are the key trade goods and commodities traded along different routes:
1. The Silk Road connected India to Central Asia and Europe. Trade goods included silk, spices (pepper, cinnamon, cardamom), precious stones, jade, tea, porcelain, and ivory. These goods contributed to the prosperity of the regions involved.
2. The maritime trade routes connected India to Southeast Asia and Africa. Trade goods traded were spices (pepper, cinnamon, cardamom), textiles, gemstones, sandalwood, ebony, and ivory. Indian traders were skilled in sailing and established economic ties with these regions.
3. The Trans-Himalayan Trade Routes connected India to China and Tibet. Trade goods included Tibetan wool, salt, horses, medicinal herbs, tea, silk, and jade. The exchange of these goods stimulated trade and facilitated cultural exchange and the spread of knowledge and ideas.
These trade goods and commodities were highly valued and played a vital role in the growth of economies, cultural exchange, and the development of trade networks. The ancient Indian trade routes facilitated the exchange of these key goods and commodities, contributing to the interconnectedness of civilizations across continents.
The Maritime Trade Routes: India’s Connection to Southeast Asia and Africa
India’s vibrant history is intricately tied to its maritime trade routes, serving as avenues for cultural exchange and economic prosperity. In this section, we explore the significance of the maritime trade routes that connected India to Southeast Asia and Africa. Discover the profound importance of maritime trade, delve into the intricate web of commerce between India and Southeast Asia, and uncover the hidden gems of trade that flourished between India and Africa. Brace yourself for a journey of trade, diversity, and interconnected civilizations.
Importance of Maritime Trade
The importance of maritime trade cannot be overstated. It played a crucial role in connecting civilizations and fostering cross-cultural interactions. In ancient Indian trade routes, maritime trade connected India to Southeast Asia and Africa, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences.
Maritime trade had significant benefits for India, including economic growth. It allowed India to access lucrative markets in Southeast Asia and Africa, leading to the expansion of trade and the growth of the Indian economy. Indian merchants traded commodities such as spices, textiles, precious metals, and gems, which were highly sought after in these regions.
Maritime trade opened doors for cultural exchange. It promoted the spread of Indian art, architecture, language, religion, and philosophical ideas to Southeast Asia and Africa, enriching the societies involved. This cultural exchange was instrumental in fostering mutual understanding and strengthening ties between civilizations.
The maritime trade routes also facilitated technological advancements. India’s navigational techniques, shipbuilding expertise, and maritime infrastructure influenced and improved the capabilities of Southeast Asian and African civilizations. It enabled the transfer of knowledge and technology between India and other regions, contributing to overall progress.
Maritime trade led to the establishment of extensive networks of ports, harbors, and trade centers along the Indian Ocean. These networks provided safe and efficient routes for ships, encouraging further trade and commercial activities. The expansion of maritime networks enhanced connectivity and facilitated the flow of goods.
Diplomatic relations were also strengthened through maritime trade. It facilitated alliances and partnerships between India and other countries, promoting political stability and ensuring the security of trade routes. It fostered peaceful cooperation among nations, contributing to a more harmonious international community.
Maritime trade played a vital role in ensuring food security for India. It allowed access to food resources from Southeast Asia and Africa, particularly commodities like rice, fruits, and spices. During times of scarcity, this access to diverse and nutritious food resources was crucial for the Indian population.
An example highlighting the importance of maritime trade is the voyage of the Ma Huan, a Chinese diplomat and translator, with Admiral Zheng He in the early 15th century. The chronicles written by Ma Huan provide valuable insights into the vibrant maritime trade networks of the time. They document the economic and cultural exchanges between China, India, and Southeast Asian countries, further emphasizing the significant impact of maritime trade in connecting civilizations and fostering cross-cultural interactions.
India and Southeast Asia: Trading spices and empowering foodies one curry at a time.
Trade between India and Southeast Asia
Trade between India and Southeast Asia has a rich history and has had a significant impact on both regions. Here are some key points about this trade:
1. Historical Connections: India and Southeast Asia have had long-standing trade connections dating back to ancient times. The exchange of goods, culture, and ideas was facilitated by maritime trade routes known as the Spice Routes.
2. Key Trade Goods: Indian textiles, such as silk, cotton, and brocade, were highly desired in Southeast Asia. Meanwhile, spices like pepper, cardamom, and cloves from Southeast Asia were in high demand in the Indian market.
3. Cultural Exchange: Trade between India and Southeast Asia not only involved the exchange of goods but also led to cultural exchanges. Hinduism and Buddhism, religions originating in India, spread to Southeast Asia through trade routes, influencing art, architecture, and religious practices.
4. Maritime Trade Routes: Maritime trade routes played a crucial role in facilitating trade between India and Southeast Asia. Indian merchants used monsoon winds to navigate the Indian Ocean, enabling efficient transportation of goods. Major trading hubs included ports like Mamallapuram and Nagapattinam in India.
5. Economic Impact: Trade between India and Southeast Asia had a significant economic impact on both regions. It led to wealth creation, the growth of trading communities, and the establishment of prosperous port cities. Indian merchants gained access to valuable commodities from Southeast Asia, enhancing their economic power.
6. Technological Exchange: Trade between India and Southeast Asia also facilitated the exchange of technology. Southeast Asian seafarers adopted Indian shipbuilding techniques and navigation methods, improving their maritime capabilities.
These aspects highlight the historical significance and impact of trade between India and Southeast Asia. The exchange of goods, cultural influences, and technological advancements strengthened the ties between these regions. Today, the legacy of ancient trade routes continues to shape the economic and cultural relationships between India and Southeast Asia.
From spices to elephants, India and Africa’s trade partnership was as wild as a safari adventure.
Trade between India and Africa
Trade between India and Africa played a role in ancient Indian trade routes. This trade was facilitated by maritime routes that connected India to various regions in Africa. India established economic and cultural exchanges with African civilizations through these routes.
Trade Goods:
- Spices: India was known for its variety of spices, including black pepper, cardamom, and cinnamon. African civilizations eagerly traded for Indian spices, using them in their cuisine and as symbols of status and wealth for African rulers.
- Textiles: India was renowned for its vibrant and intricate textiles. African civilizations valued Indian textiles for their quality and craftsmanship, using them for clothing, adornments, and trade. Indian textiles became a part of African cultural identity and indicators of social status.
- Gold: India had a constant demand for gold, and African civilizations were rich in this precious metal. African civilizations traded their abundant gold reserves with India for goods such as spices, textiles, and luxury items, contributing to the flourishing of African economies.
- Ivory: India desired ivory for its exquisite craftsmanship and religious artifacts. African civilizations provided a steady supply of ivory primarily sourced from elephants. African ivory was highly prized in India and transformed into intricate carvings, statues, and jewelry. The trade of ivory between India and Africa led to artistic and cultural exchanges.
The trade between India and Africa enriched both regions economically and fostered cultural connections. The exchange of goods and ideas facilitated the spread of knowledge and influenced art, architecture, and religious practices. This trade relationship created a bridge between the diverse civilizations of India and Africa, shaping their histories and leaving a lasting legacy.
The Trans-Himalayan Trade Routes: India’s Connection to China and Tibet

Photo Credits: Thegeopoliticalobserver.Com by Scott Harris
Journey across ancient trade routes that linked India to China and Tibet. Discover the vibrant exchanges of goods, ideas, and culture that blossomed along these historic pathways. Explore an overview of the Trans-Himalayan Trade Routes, delve into India’s intriguing interactions with China and Tibet, and uncover the rich tapestry of trade goods and cultural exchange that shaped the region’s history. Step into the footsteps of merchants and traders as we unravel the fascinating stories of this vital connection between civilizations across continents.
Overview of the Trans-Himalayan Trade Routes
The Trans-Himalayan trade routes, which connected ancient India with China and Tibet, were a network of paths and trails that traversed the Himalayan mountain range. These routes played a crucial role in facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture between civilizations.
India had extensive interactions with China and Tibet through these trade routes. Traders and travelers braved challenging terrains and harsh weather conditions to engage in commercial activities and cultural exchange.
A wide range of commodities, such as spices, precious metals, silk, tea, and medicinal herbs, were traded along these routes, leading to economic prosperity and regional cooperation.
The trade routes had a significant impact on social and cultural aspects. They served as conduits for the exchange of languages, religions, artistic styles, and intellectual ideas.
Notably, these routes also facilitated technological and intellectual exchange. Knowledge about agriculture, architecture, medicine, and astronomy was shared among the different societies.
The Trans-Himalayan trade routes were an integral part of the ancient Indian trade networks. By connecting India with China and Tibet, they promoted economic, social, and cultural exchange. Understanding the historical significance of these routes helps us grasp the interconnectedness of ancient societies and their contributions to the development of human civilization.
For a deeper understanding of the historical connections between India, China, and Tibet, exploring the Trans-Himalayan trade routes provides valuable insights. Investigating the trade networks and the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture along these routes will give you a comprehensive overview of ancient societies.
India’s interaction with China and Tibet: where curry meets yak butter tea, creating a blend of flavors and cultures that transcends borders.
India’s Interaction with China and Tibet
India’s interaction with China and Tibet was extensive and beneficial, encompassing various aspects such as economic ties, cultural exchange, technological advancements, diplomatic relations, and strategic importance.
Economic ties played a crucial role in India’s interaction with China and Tibet. The trade between these regions involved the exchange of silk, spices, tea, and precious metals, resulting in the establishment of prosperous commercial centers. This economic relationship contributed to the growth and development of the involved parties.
Apart from economic ties, the interaction between India, China, and Tibet also led to a deep cultural exchange. Buddhism, for instance, spread from India to China and Tibet through these trade routes, highlighting the significant influence that these interactions had on their respective cultures. This cultural exchange extended to art, architecture, and philosophy, with Indian and Chinese traditions mutually influencing each other.
India’s interaction with China and Tibet facilitated the exchange of technological advancements. India shared its knowledge of metallurgy, shipbuilding, and agriculture with these regions, contributing to their technological growth. In return, China influenced India in areas such as papermaking and printing techniques, resulting in the enrichment of both societies.
Diplomatic ties were another important aspect of India’s interaction with China and Tibet. These ties were often established through marriages and missions between royal families, creating a sense of peace and understanding along the trade routes. The establishment of diplomatic relations helped maintain stability and fostered cooperation between the parties involved.
The interaction between India, China, and Tibet held strategic importance due to the Trans-Himalayan trade routes. These routes served as crucial links between India and the Far East, facilitating the flow of goods and ideas. Consequently, political alliances and cultural exchange flourished, further enhancing the significance of these interactions.
For those interested, visiting historical sites along the ancient trade routes or delving into the artwork, literature, and philosophy that emerged from this historical exchange can provide profound insights. The journey through this rich historical exchange is enlightening and captivating, offering a deeper understanding of the dynamics between India, China, and Tibet.
Trade Goods and Cultural Exchange
The ancient Indian trade routes facilitated the exchange of goods and cultural interaction among civilizations. Various trade goods were exchanged during this time, including spices from South India, silk from China, cotton textiles from Gujarat, precious stones from Rajasthan, ivory from Kerala, perfumes from Persia, incense from the Malabar Coast, and tea from Assam.
These trade goods had economic value and cultural significance. For example, the introduction of silk from China to India led to the development of weaving techniques and the production of fine silk textiles. The exchange of spices influenced cuisines, traditional medicine, and religious ceremonies.
Cultural exchange also involved the sharing of ideas, beliefs, practices, languages, literature, and music. Buddhism, originating in India, spread to other parts of Asia through these trade routes, impacting religious beliefs, art, architecture, and philosophy.
The ancient Indian trade routes shaped civilizations and contributed to the development of technologies, artistic techniques, and intellectual pursuits. Today, we can still see the legacy of this trade and cultural exchange, as it connected civilizations across continents.
Impact and Legacy of Ancient Indian Trade Routes
The impact and legacy of ancient Indian trade routes continue to resonate across continents, influencing economies, societies, cultures, and intellectual exchange. Delving into the sub-sections, we will uncover the economic benefits that these trade routes brought, the profound social and cultural transformations they facilitated, and the invaluable technological and intellectual exchanges that shaped the world we know today. Brace yourself for a journey that unravels the interconnectedness of civilizations, as we explore the remarkable impact of these ancient trading networks.
Economic Impact
The ancient Indian trade routes greatly influenced the economy of the regions involved. Here are the specific impacts of these trade routes:
1. Facilitated Goods Exchange: The trade routes allowed for the exchange of various goods, promoting commerce on a large scale. Key trade commodities, such as spices, textiles, precious metals, gems, and luxury items, were highly sought after, driving economic growth in both India and its trading partners.
2. Boosted Regional and International Trade: The trade routes connected India with Central Asia, Europe, Southeast Asia, and Africa, fostering extensive regional and international trade networks. This increased commercial activity led to the growth of towns and cities along the routes, stimulating economic prosperity.
3. Created Employment Opportunities: The expansion of trade along these routes created new employment opportunities for merchants, traders, artisans, and laborers. Caravanserais and maritime ports flourished as crucial economic hubs, providing employment to a diverse range of individuals and contributing to economic development.
4. Spurred Urbanization and Infrastructure Development: The economic benefits from trade resulted in the growth of urban centers and infrastructure development. Cities like Taxila, Varanasi, and Madurai became important trading hubs, attracting merchants and traders from far and wide. Ports and harbors were built along the coastlines, facilitating maritime trade and enhancing connectivity.
5. Stimulated Innovation and Technological Advances: The exchange of goods, knowledge, and ideas along these trade routes contributed to innovation and technological advancements. For instance, the trade in textiles led to the refinement of weaving techniques, while the demand for spices encouraged the development of preservation and packaging methods. Ancient Indian Trade Routes: Connecting Civilizations Across Continents
6. Fostered Cultural Exchange: The economic interactions along these trade routes resulted in the exchange of goods, language, art, religion, and philosophy. This cross-cultural exchange enriched societies and contributed to the growth of civilizations, fostering social and intellectual advancements.
Social and Cultural Impact
The ancient Indian trade routes had a significant social and cultural impact, incorporating the exchange of ideas, beliefs, and practices between civilizations across continents. Not only did these trade routes exchange goods, but they also facilitated the exchange of knowledge, ideas, and cultural practices, leading to cultural assimilation and the spread of Indian traditions.
Indian traders and travelers interacted with people from diverse linguistic and religious backgrounds along the trade routes, resulting in the diffusion of Indian languages like Sanskrit and Pali, as well as the spread of Buddhism and Hinduism to regions like Central Asia, Southeast Asia, and China.
The trade routes enabled the exchange of artistic styles and architectural techniques, with Indian influences seen in the Buddhist monuments of Southeast Asia, the cave temples of Central Asia, and the pagodas of China.
The trade routes allowed for the exchange of spices, herbs, and culinary techniques, with Indian spices like black pepper, cardamom, and cinnamon influencing the cuisines of different regions. Cooking techniques were also shared, resulting in a fusion of flavors and the creation of new dishes.
In terms of education and intellectual exchange, the trade routes played a significant role in the transmission of knowledge. Scholars from around the world came to Indian universities and centers of learning to study subjects like astronomy, mathematics, medicine, and philosophy, enriching their own societies.
The interaction of different cultures along the trade routes fostered a sense of unity and cosmopolitanism, promoting tolerance and understanding among diverse people and leading to cultural syncretism and social cohesion.
Technological and Intellectual Exchange
The ancient Indian trade routes were instrumental in promoting technological and intellectual exchange between civilizations. Through these routes, ideas, knowledge, inventions, and innovations were shared, leading to significant advancements in various fields.
1. Exchange of Scientific Knowledge: The trade routes played a crucial role in facilitating the exchange of scientific knowledge between different regions. Influential Indian scholars such as Aryabhata and Brahmagupta made noteworthy contributions to mathematics and astronomy, which had a profound impact on scholars in Central Asia and Europe.
2. Spread of Buddhism and Hinduism: In addition to scientific knowledge, the trade routes also paved the way for the spread of Buddhism and Hinduism. Buddhist monks and scholars traveled along these routes, disseminating their teachings and sacred scriptures. This, in turn, resulted in the establishment of Buddhist monasteries and centers of learning, fostering intellectual discourse and the dissemination of knowledge.
3. Transmission of Literature and Philosophy: The trade routes acted as conduits for the transmission of literary works and philosophical ideas. Epic Indian tales such as the Ramayana and Mahabharata were transported across continents through both oral tradition and written manuscripts, greatly influencing the cultural and intellectual development of societies.
4. Technological Innovations: The trade routes played a key role in facilitating the exchange of technological innovations. For instance, India’s expertise in iron smelting and production was shared with Central Asia and China, leading to advancements in metallurgy in those regions.
5. Cultural Exchange: The trade routes fostered a vibrant cultural exchange among civilizations. The interaction between traders, scholars, and travelers from diverse backgrounds resulted in the blending of customs, languages, art forms, and religious practices. This cultural synthesis greatly enriched the intellectual vibrancy of societies situated along the trade routes.
6. Mathematical and Astronomical Instruments: The trade routes also facilitated the diffusion of mathematical and astronomical instruments. Indian mathematicians and astronomers developed sophisticated instruments like the astrolabe, which accurately measured celestial positions. These instruments were adopted by other civilizations, significantly enhancing their understanding of astronomy and navigation.
Some Facts About Ancient Indian Trade Routes: Connecting Civilizations Across Continents:
- ✅ Indian Ocean trade routes have been vital in connecting civilizations across continents for centuries. (Source: study.com)
- ✅ The Silk Route, Spice Routes, and Incense Route were major ancient Indian trade routes that facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between Europe and Asia. (Source: metmuseum.org)
- ✅ The Indian Ocean trade network played a significant role in the transmission of raw materials, foodstuffs, luxury goods, and technology between different regions. (Source: odysseytraveller.com)
- ✅ Trade routes like the Amber Road, Persian Royal Road, and Roman Road Network connected India to various parts of the world, enabling the flow of goods and fostering cultural interactions. (Source: odysseytraveller.com)
- ✅ The Indian Ocean trade routes saw the flourishing of cities and port towns, such as Palmyra, Petra, and Muziris, which became hubs of trade and cultural exchange. (Source: en.wikipedia.org)
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How did ancient Indian trade routes connect civilizations across continents?
Ancient Indian trade routes connected civilizations across continents by facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences between different regions. These trade routes, such as the Silk Route and the Indian Ocean trade network, allowed for the transfer of raw materials, luxury goods, and foodstuffs from areas with surpluses to areas in need. They also served as communication highways, transmitting new inventions, religious beliefs, artistic styles, languages, and social customs.
2. What were some notable ancient Indian trade routes?
Some notable ancient Indian trade routes include the Silk Route, which connected East Asia with South Asia, Persia, the Arabian Peninsula, East Africa, and Southern Europe, and the Indian Ocean trade network. The Indian Ocean trade routes connected the Middle East and Africa to East Asia, and involved the exchange of goods from Persia and the Turkish Caliphates for items in Africa, India, and China. Other trade routes included the Incense Route, Persian Royal Road, Roman Road Network, and Australian Aboriginal Trading Routes.
3. How did the Indian Ocean trade routes contribute to the rise of civilizations?
The Indian Ocean trade routes played a crucial role in the rise of civilizations by facilitating the exchange of wealth, knowledge, and cultural influences. These trade routes allowed different civilizations to access valuable resources and goods from distant regions, which contributed to economic growth and the development of prosperous trading cities. The trade routes also allowed for the transmission of ideas, religions, artistic styles, and technologies, leading to cultural enrichment and the formation of cosmopolitan centers along the trade routes.
4. What were the main trade goods exchanged along ancient Indian trade routes?
A variety of trade goods were exchanged along ancient Indian trade routes. Some of the main goods included silk from China, spices from South Asia, frankincense and myrrh from Arabia, spices from India, and gold and slaves from Africa. Other goods exchanged included jewels, amber, animal furs and skins, raw materials, and luxury items. The trade routes facilitated the movement of these goods from areas of surplus to areas of demand, creating a dynamic zone of interaction and commerce.
5. How did maritime technology contribute to ancient Indian trade routes?
Maritime technology, such as plank-built watercraft, played a significant role in the development and success of ancient Indian trade routes. These advanced boats enabled long-distance sea trade, allowing for the transport of goods across the Indian Ocean and other bodies of water. Coastal settlements along the trade routes served as trading outposts and provided necessary services to merchants, further facilitating trade and cultural exchange.
6. How did ancient Indian trade routes influence artistic exchanges?
Ancient Indian trade routes had a profound impact on artistic exchanges between different civilizations. Cities along these trade routes, such as Palmyra, Petra, and Swahili city-states, became centers of cultural interaction, where people from different backgrounds could come together. The transmission of goods, ideas, and cultural influences along the trade routes led to the blending of artistic styles. For example, the sculptural styles of Gandhara in modern-day Pakistan and northern India were influenced by Hellenistic styles popularized by the Romans, showcasing the cross-cultural artistic exchanges facilitated by trade.
[…] article delves into the subject by exploring different periods of Indian history and examining how Indian philosophies influenced the social structure, political systems, formation of empires, governance, and even the […]
[…] problem of unemployment in India is a complex challenge with wide-ranging impacts. It requires collaborative efforts from government, businesses, and […]