Introduction
India is a country with various languages, cultures and traditions, is home to an impressive historical record that has developed over the course of millennia. From the earliest times until the modern age The time line that is Indian time is an testimony to the enduring as well as the growth and development of an entire nation. In this article, we set off on an unforgettable trip through time, examining the fascinating historical events, dynasties, changes and landmarks that have been the driving force behind the history of India’s past.
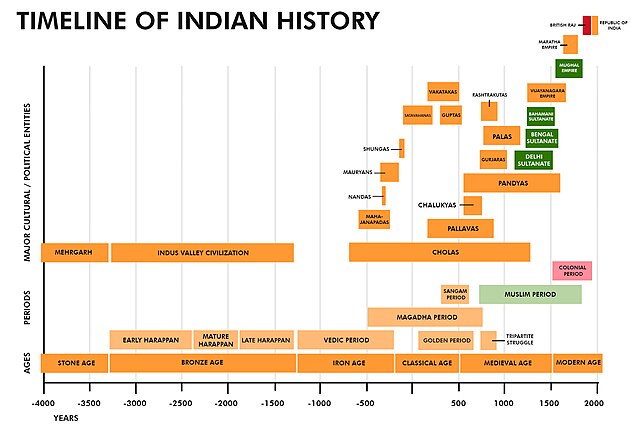
The Ancient Roots (5000 BCE – 600 CE)
The long and rich background of India is defined by the fall and rise of great civilizations that each contributed to the diverse culture that is the basis of India in the present.
The Indus Valley Civilization: Cradle of Civilization

The chronology of Indian history starts with the mysterious Indus Valley Civilization that flourished from 3300 BCE until 1300 BCE. It was located along the banks of the Indus River, this sophisticated urban civilization left stunning architectural remains as well as the system of writing that is still a mystery to historians.
Vedic Period: Wisdom found in Scriptures
In this time (1500 BCE – 500 BCE) In this time, the sacred text called the Vedas were written, offering insight into the religious, social and philosophical beliefs held by the early Indians.
Mauryan Empire: Unifying the Subcontinent
In 322 BCE, the The Emperor Chandragupta Maurya founded the Mauryan Empire, which was an Indian state that was the very first to be pan-Indian. The famous leader Ashoka the Great was a proponent of Buddhism and is famous for his edicts that emphasized moral principles.
Gupta Dynasty: The Golden Age
From the 4th through the 6th century CE From the 4th to the 6th century CE, the Gupta Dynasty flourished, ushering into a period of scientific, artistic and literary triumphs. The idea of zero complex temple architecture and the enduring Kalidasa’s works are just a few of the Gupta time’s accomplishments.
Medieval Marvels (600 CE – 1700 CE)
The period of the medieval era in India saw the rising of powerful dynasties, the expansion of Islam and the integration of different styles of life.
Chola Dynasty: Naval Supremacy and Artistic Splendor
The Cholas (9th – 13th century CE) were famous for their maritime skills as well as their extensive trade networks and architectural marvels such as Brihadeeswarar Temple. Brihadeeswarar Temple.
Delhi Sultanate: The Arrival of Islam
After the Ghurid invasions of the 12th century and the 12th century, the Delhi Sultanate was established, which marked a significant change in both the political and social landscape. In the 12th century, Qutub Minar and Alai Darwaza are a testament to this time.
Mughal Empire: The Fusion of Cultures
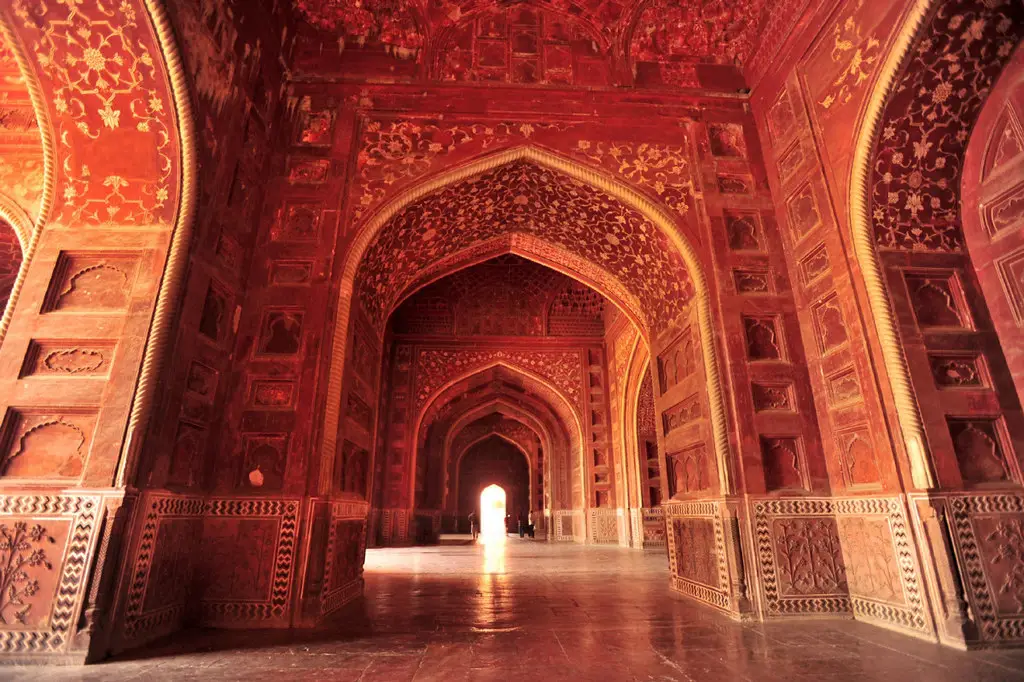

The Mughal Empire (16th – 19th century CE) witnessed the height of Indian art and architecture, as demonstrated in The Taj Mahal. Akbar’s policies of religious tolerance as well as its syncretic Bhakti movement are lasting legacies.
The Maratha Confederacy: Great Power
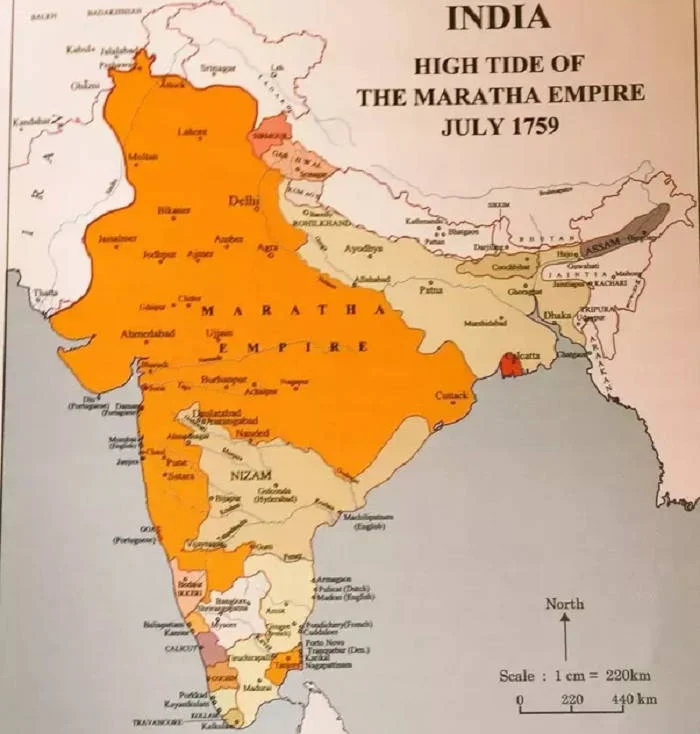
The Marathas became a major power during the period of 17th-century, threatening Mughal supremacy. Shivaji was the king of the Maratha Empire, is praised for his strategic knowledge.
Colonial Struggles and Independence (1700 CE from 1700 CE to 1947 CE)
The course of Indian history takes an important direction as the subcontinent is transformed into a battlefield for European colonial power and Indian freedom movements gain momentum. Indian freedom movement grows in strength.
British Colonialism: Impact and Resistance
The East India Company’s influence was growing gradually, resulting in the expansion of colonization in India. It was the First War of Independence in 1857 was a major protest to British rule.
Indian National Congress: A United Front
The Indian National Congress, founded in 1885, was the driving force behind the fight for independence. The leaders such as Mahatma Gandhi utilized non-violent methods to fight British authorities.
Partition of India: A Sweet Freedom
1947 saw the conclusion of the Indian Independence movement and the division of subcontinental India into India as well as Pakistan. This time was characterized by massive political turmoil and a massive influx of people.
Modern India (1947 CE – Present)
Its timeline in Indian time extends into the present day, and is characterized by the country’s efforts for its establishment as a pluralistic, democratic and prosperous nation.
Nehruvian Era: Nation-Building and Industrialization
Under the direction by Jawaharlal Nehru’s leadership, India embarked on a process of modernization and industrialization. The creation of a republic that was democratic laid the foundation for a brand new India.
Green Revolution: Agricultural Transformation
Through the 60s and 1970s, in the 1960s and 70s, Green Revolution transformed India’s agriculture and led to a rise in food production and self-sufficiency.
Economic Liberalization: Open New Horizons
As of 1991, India introduced economic reforms that reformed its economy, which led to an increase in international investment and technological advances.
India as a 21st Century A Global Player
Presently, India is a burgeoning global power, with accomplishments in science and technology, space exploration and a variety of cultural contributions.
FAQs
What is the significance of the Indus Valley Civilization in Indian history?
The Indus Valley Civilization holds immense importance as one of the earliest urban cultures, providing insights into ancient urban planning, trade networks, and a mysterious script that still eludes deciphering.
How did Mahatma Gandhi influence India’s struggle for independence?
Mahatma Gandhi’s philosophy of nonviolent resistance, or “Satyagraha,” played a pivotal role in India’s fight for freedom. His leadership and moral principles inspired millions to participate in the movement.
What led to the partition of India in 1947?
The partition of India was a result of religious and political tensions between Hindus and Muslims. The two-nation theory led to the creation of India and Pakistan as separate nations.
What are some notable achievements of modern India?
Modern India has excelled in various fields, from space research (ISRO) and information technology to the arts and cinema. It continues to be a vibrant democracy with a diverse cultural heritage.
Conclusion
The timeline of Indian history is a captivating journey through the ages, marked by profound shifts, achievements, and challenges. From ancient civilizations to modern aspirations, India’s history is a testament to the resilience and dynamism of its people. As we reflect on this diverse tapestry, we recognize the importance of understanding the past to shape a brighter future.