Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Ancient Education Systems in India
- Gurukula System
- Buddhist Education
- Nalanda and Taxila Universities
- Medieval Education
- Islamic Influence on Education
- Colonial Period and Western Education
- Modern Education Reforms
- Current Education System in India
- Challenges and Issues
- Government Initiatives
- Future Prospects
- Conclusion
- FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Introduction
Education in India is long and varied history that goes back to the millennia. The Indian subcontinent is the source of numerous educational concepts and institutions, which makes it a significant source of knowledge and education. This article traces the fascinating story of Indian education from the earliest times to present and highlights its most significant landmarks, influences, and the challenges.
Ancient Education Systems in India
The earliest roots in Indian educational system can be traced to the earliest times, when knowledge was transmitted through a variety of traditional methods. At the time the majority of education was conducted in gurukulas. They were residential schools in which students resided with their teachers. Gurukulas were based on holistic learning and focused not just on academics, but also character development moral values and life abilities.
Gurukula System
Gurukul was popular throughout the Vedic period and played a significant influence on the spiritual and intellectual growth of students. In these gurukuls students were given individualized attention by their Gurus (teachers) and learnt by close interaction and watching. The curriculum was comprised of subjects like math, astronomy writing, philosophy, and war.
Buddhist Education
In the period in the reign of Lord Buddha, Buddhist monasteries emerged as educational centers. The monastic system of education provided training to monks and lay people. Buddhist universities, like Nalanda and Taxila were famous centers of learning and attracted scholars from all areas of the globe.
Nalanda and Taxila Universities
Nalanda along with Taxila Universities flourished during the Gupta period, and attracted scholars from many fields, including astronomy mathematics medicine, philosophy, and astronomy. They had libraries that were well-established and lecture halls as well as a robust education system that encouraged intellectual discussion and critical thinking.
Medieval Education
Since the emergence of Islamic rule in India the system of education was subject to significant changes. Islamic scholars established madrasas that focused on Islamic Theology as well as religious study. The curriculum contained subjects such as Arabic, Persian, Islamic law and Quranic studies.
Islamic Influence on Education
The Islamic period saw the creation of renowned centers of learning including The Madrasa from Ghazni in Ghazni and Madrasa in Delhi. These centers became major centres for higher education, and played a significant part in spreading knowledge.
Colonial Period and Western Education
The introduction of European colonial powers in India especially the British and the British, led to an important change in the system of education. In the early years, British introduced a Western-style educational system that emphasized English science, language education and the latest subjects. The creation of colleges, universities and schools opened the way to a more organized and formalized system of education.
Modern Education Reforms
After independence, India witnessed several educational changes aimed at providing a quality education for its citizens. It was the Kothari Commission of 1964 laid the foundations for education planning and introduced the idea of a system that was 10+2+3, that is still in use in the present. The government also concentrated on the promotion of technological education as well as higher-education and vocational education to satisfy the needs of a rapidly growing economy.
Current Education System in India
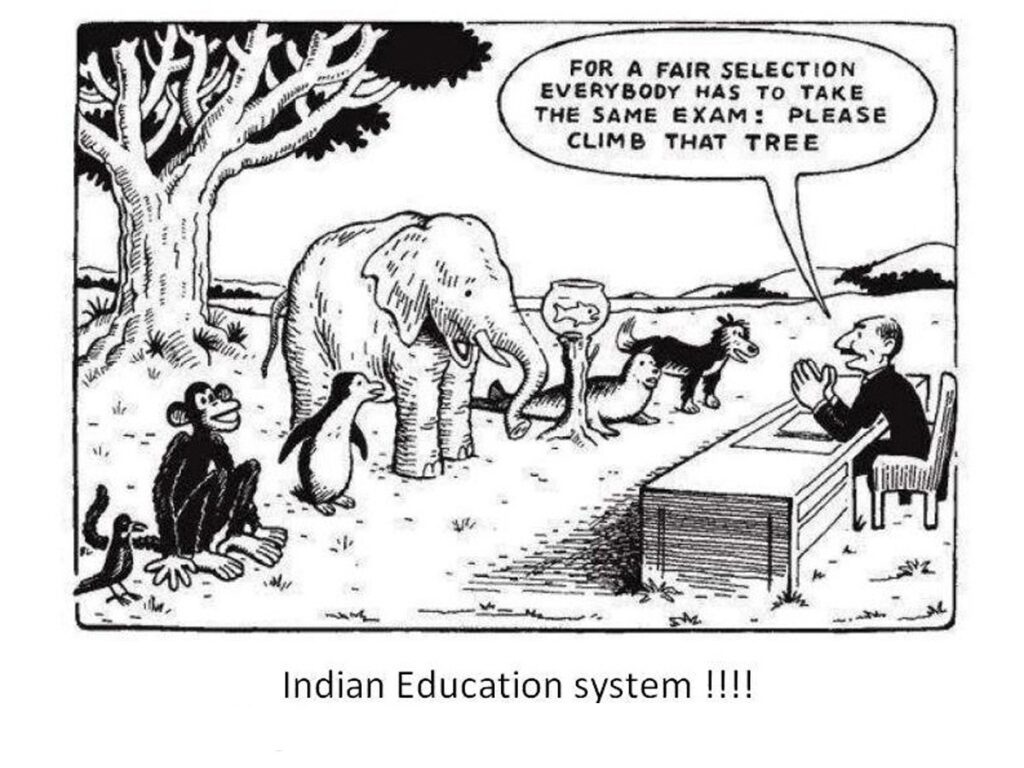
The education system currently in India is extensive and varied that includes schools, colleges universities, specialized institutions. It has a broad curriculum that covers co-curricular and academic subjects and skills development programs. However, the system has issues such as a high teacher-to-student ratio, insufficient infrastructure, and inequalities in access to education in different regions.
Challenges and Issues
Despite the advancements made in the area of education India is facing a variety of challenges. This includes a demand for a better quality of education and tackling the divide between rural and urban as well as reducing dropout rates. increasing teacher education programs, and incorporating new teaching methods.
Government Initiatives
The Indian government has rolled out a variety of initiatives to tackle the issues in the field of education. Initiatives such as Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan as well as Atal Tinkering Labs aim to enhance access, quality and the quality of education. This policy National Education Policy 2020 also offers a roadmap to transform the system of education to meet the ever-changing demands of students.
Future Prospects

Future of Indian education is full of potential. With the rapid growth of technology, there’s a growing emphasis on digital learning and online education as well as skills development. The emphasis of the government on entrepreneurship and vocational training is to provide students with the skills needed to be competitive in the job market.
Conclusion
The rich history of Indian education is a testimony to the nation’s rich intellectual heritage as well as its dedication to spreading knowledge. From the ancient gurukulas, to modern colleges and schools, the education system in India has changed to keep pace with the changing world. Even as challenges remain, concerted efforts by both the government and society will lead to a an improved future where each person has access high-quality education.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is the age of this system? Indian educational system?
It is believed that the Indian school system has an rich history that spans many thousands of years including the ancient Gurukula system as one of its first types.
2. What were the most renowned universities in the ancient India?
Nalanda along with Taxila were two renowned institutions in ancient India that attracted scholars from all over the globe.
3. What are the major issues facing those in the Indian educational system?
The Indian education system is faced with issues like inadequate infrastructure, a high teacher-to-student ratio, and a lack of the access of education.
4. What are the government’s initiatives to enhance the education system in India?
It is the Indian government has launched programs such as Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan as well as Atal Tinkering Labs to improve the accessibility to education and improve its quality.
5. What’s the future of Indian education?
The next phase of Indian education is in the embracing of digital learning in the form of online education, online education, and the process of skill development to meet the changing demands of students.

[…] education. Let’s embark on a journey through time to explore the historical overview of women’s education in India and witness the transformative power of […]