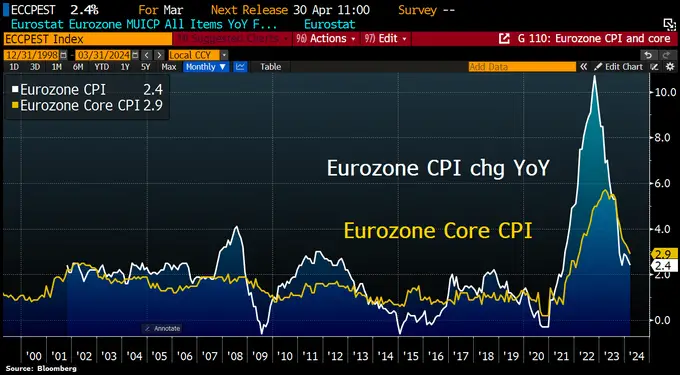
The latest inflation data from the Eurozone has sparked speculation about the possibility of a rate cut by the European Central Bank (ECB) in June. According to Holger Zschaepitz, a market analyst and author, the headline consumer price index (CPI) in the Eurozone slowed to 2.4% year-over-year in March, down from 2.6% in February. This figure came in below the consensus forecast of 2.5%.
Core Inflation Moderates to Lowest Level in Over Two Years
The core CPI, which excludes volatile components like food and energy, also decelerated to 2.9% from 3.1% in the previous month. This reading was again lower than economists’ expectations, marking the lowest level in more than two years.
Signs of Persistent Inflationary Pressures in Service Sector
However, the data revealed that inflationary pressures have yet to ease in labor-intensive service industries. Service price inflation remained unchanged at 4.0% year-over-year for the fifth consecutive month, indicating that wage pressures and sticky price dynamics continue to pose challenges.
Implications for Monetary Policy
The cooling inflation figures have fueled speculation that the ECB might consider a rate cut at its June meeting. However, the central bank will likely weigh the moderation in headline and core inflation against the persistent service sector price pressures and the overall economic outlook.
Balancing Act for the ECB
The ECB faces a delicate balancing act as it navigates the path towards price stability. On one hand, the easing of overall inflation could prompt the central bank to adopt a more accommodative stance to support economic growth. On the other hand, the stubbornly high service sector inflation and the potential for second-round effects could compel the ECB to maintain a hawkish stance for a longer period.
Labor Market Dynamics and Wage Growth
#Eurozone #inflation cools, setting stage for June rate cut: Headline CPI slowed to 2.4% YoY in March from 2.6% in Feb below consensus forecast of 2.5%. Core CPI slowed to 2.9% from 3.1%, again below economists' expectations to reach lowest level in >2yrs. But there were signs… pic.twitter.com/3qfiu2LIvm
— Holger Zschaepitz (@Schuldensuehner) April 3, 2024
Labor market dynamics and wage growth will be crucial factors in the ECB’s decision-making process. If wage growth continues to accelerate, it could fuel further inflationary pressures, particularly in the service sector, making it more challenging for the central bank to ease monetary policy.
Potential Sectoral Divergences
Analysts have also warned about the possibility of sectoral divergences in inflation dynamics. While some sectors may experience deflation, others could remain trapped in an inflationary spiral, further complicating the ECB’s task of achieving price stability across the Eurozone.
Global Economic Outlook and External Factors
External factors, such as the global economic outlook, geopolitical tensions, and commodity price fluctuations, will also play a role in shaping the ECB’s policy decisions. A deteriorating global economic environment or supply chain disruptions could exacerbate inflationary pressures, prompting the central bank to maintain a tighter monetary policy stance.
Conclusion
The recent cooling of Eurozone inflation has reignited the debate around potential rate cuts by the ECB. However, the central bank will need to carefully assess the underlying drivers of inflation, including service sector dynamics, labor market conditions, and external factors, before making any policy adjustments. As the economic landscape continues to evolve, the ECB’s decision-making process will remain a delicate balancing act, with implications for both price stability and economic growth across the Eurozone.