Ancient India is known for its rich history and diverse civilizations that have impacted the subcontinent’s cultural and social fabric. From the sophisticated urban planning of the Indus Valley Civilization to the golden age of the Gupta Empire, each period has contributed significantly to India’s heritage. This article will delve into the critical ancient Indian civilizations, their unique features, and their lasting legacies.
Introduction
Ancient Indian civilizations are some of the oldest in the world, with evidence of human settlements dating back thousands of years. These civilizations flourished along the banks of major rivers and witnessed remarkable advancements in various fields, including urban planning, literature, science, and governance.
Indus Valley Civilization
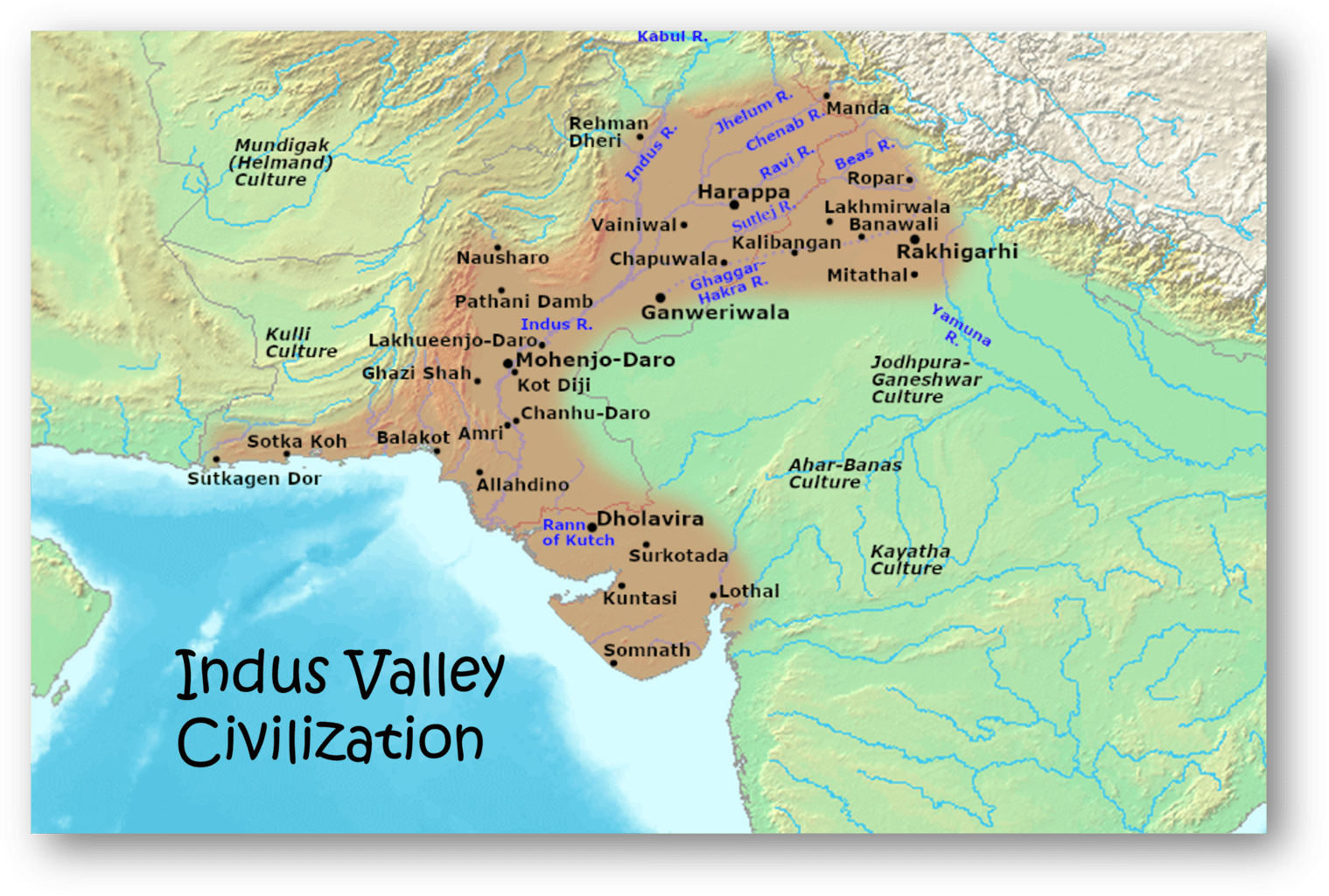
The Indus Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan Civilization, was one of the world’s earliest urban societies. It emerged around 2600 BCE and thrived in the fertile plains of the Indus River in present-day Pakistan and western India. The cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro were the centerpieces of this civilization.
Location and Period
The Indus Valley Civilization extended a vast area, covering parts of modern-day India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan. It existed for approximately 700 years, from 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE.
Urban Planning and Architecture
The cities of the Indus Valley Civilization were meticulously planned, with well-organized street grids, advanced drainage systems, and multi-story houses made of baked bricks. The Great Bath, a large public bathing complex, is a testament to their architectural prowess.
Economy and Trade
The people of the Indus Valley engaged in agriculture, trading various goods such as cotton, pottery, and beads. They established trade links with Mesopotamia, Oman, and other regions, contributing to their economic prosperity.
Vedic Period
The Vedic Period marks the arrival of the Indo-Aryans in the Indian subcontinent. It is characterized by the composition of the Vedas, a collection of ancient scriptures that form the basis of Hindu religious and philosophical traditions.
The arrival of the Aryans
The Indo-Aryans migrated to the Indian subcontinent around 1500 BCE and brought their language, Sanskrit, and a complex social and religious system. They gradually settled in different regions and established a new way of life.
Vedic Literature and Culture
The Vedas, composed during this period, contain hymns, prayers, rituals, and philosophical discourses. They provide insights into ancient India’s social, religious, and cultural practices. The caste system, with its four main varnas (classes), also originated during this period.
Social and Political Structures
The Vedic society was organized into various clans and tribes known as “Janas.” These tribes often engaged in warfare and conflicts over resources. The rajas (chieftains) emerged as the political leaders during this time.
Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, founded by Chandragupta Maurya, was the first major empire in ancient India. It emerged in the 4th century BCE and expanded its territories to encompass most of the Indian subcontinent.
Rise of the Mauryan Dynasty
Chandragupta Maurya established the empire by overthrowing the Nanda Dynasty. Under the rule of his successor, Emperor Bindusara, and later Emperor Ashoka, the Maurya Empire reached its zenith, encompassing a vast and diverse region.
Emperor Ashoka
Emperor Ashoka, known as Ashoka the Great, is renowned for transforming from a ruthless conqueror to a benevolent ruler. After witnessing the horrors of war, he embraced Buddhism and adopted a non-violence and religious tolerance policy. Ashoka’s rock edicts, inscribed across the empire, provide valuable insights into his governance principles and moral teachings.
Contributions and Legacy
The Maurya Empire made significant contributions to various aspects of ancient Indian society. Ashoka’s efforts to promote Buddhism and build monasteries led to the spread of the religion throughout Asia. The empire also played a crucial role in enhancing trade and communication networks, fostering cultural exchanges between regions.
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire is often called the “Golden Age” of ancient India. It flourished from the 4th to the 6th century CE, encompassing a period of outstanding achievements in science, mathematics, art, and literature.
Golden Age of Indian History
Under the Gupta rulers, India experienced remarkable art, literature, and scientific advancements. Scholars and intellectuals thrived during this period, contributing to the development of various disciplines. The Gupta Empire was known for its patronage of learning and the arts.
Achievements in Science, Mathematics, and Literature
During the Gupta era, Indian scholars made groundbreaking discoveries in mathematics, including the concept of zero, the decimal system, and the numerical value of pi. The famous mathematician Aryabhata and the renowned astronomer Brahmagupta were products of this golden age. Literature flourished with notable works like Kalidasa’s plays and the compilation of the great epics Ramayana and Mahabharata.
Decline and Fall
The Gupta Empire gradually declined due to internal conflicts, invasions, and regional fragmentation. By the 6th century CE, the empire disintegrated, paving the way for provincial kingdoms to emerge across the Indian subcontinent.
Conclusion
Ancient Indian civilizations, such as the Indus Valley Civilization, the Vedic Period, the Maurya Empire, and the Gupta Empire, have played a crucial role in shaping India’s cultural, social, and intellectual landscape. From the Indus Valley’s advanced urban planning to the Gupta Empire’s academic achievements, these civilizations have left a lasting legacy that continues to inspire and influence present-day Indian society.
FAQs
1. What is the significance of the Indus Valley Civilization? The Indus Valley Civilization was significant for its well-planned cities, advanced infrastructure, and trade connections, showcasing ancient India’s early urbanization and cultural sophistication.
2. How did the Vedic Period contribute to Indian society? The Vedic Period laid the foundations of Hinduism, introduced Sanskrit as a classical language, and established the caste system, profoundly impacting Indian culture.
[…] A Brief Overview of Ancient Indian Civilizations […]
[…] Indus Valley Civilization (also referred to as The Harappan Civilization, flourished around 2600 and around 1900 BCE within […]
[…] is believed that the Indus Valley Civilization which dates in the early 3rd millennium BCE is one of the first urban civilizations in the […]